Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the limitations of Ohm’s law.
उत्तर
There are two main limitations:
(i) Temperature,
(ii) Physical condition of the conductor.
It is found that the ratio V/I is mo longer constant when the temperature is not kept constant. Generally, resistance increases with the rise in the temperature of the conductor.
Physical conditions of any conductor mainly include:
(i) Its length,
(ii) Its cross-sectional area,
(iii) The kind of material.
If there is no change in any of the above three conditions and also other condition like temperature remains constant, then Ohm’s law holds good, i.e., the ratio V/I remains constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Ohm's law gives a relationship between:
(a) current and resistance
(b) resistance and potential difference
(c) potential difference and electric charge
(d) current and potential difference
What is the necessary condition for a conductor to obey Ohm’s law?
- Draw a V-I graph for a conductor obeying Ohm’s law.
- What does the slope of V–I graph for a conductor represent?
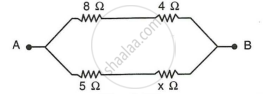
In the circuit shown below in Fig, calculate the value of x if the equivalent resistance between A and B is 4 Ω.
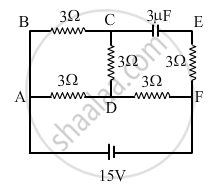
In the circuit shown in the figure, find the total resistance of the circuit and the current in the arm AD.
A wire has a length of 2.0 m and a resistance of 5.0 Ω. Find the electric field existing inside the wire if it carries a current of 10 A.
How does an increase in the temperature affect the specific resistance of a :
(i) Metal and
(ii) Semiconductor ?
A wire connected to a power supply of 230 V has power dissipation P1. Suppose the wire is cut into two equal pieces and connected parallel to the same power supply. In this case, power dissipation is P2. The ratio of `"P"_2/"P"_1` is
What is non ohmic device?

Calculate the total resistance of the circuit and find the total current in the circuit.
