Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the restrictions for having images produced by spherical mirrors to be appreciably clear.
उत्तर
- In order to obtain clear images, the formulae for image formation by mirrors or lens follow the given assumptions:
- Objects and images are situated close to the principal axis.
- Rays diverging from the objects are confined to a cone of a very small angle.
- If there is a parallel beam of rays, it is paraxial, i.e., parallel and close to the principal axis.
- In case of spherical mirrors (excluding small aperture spherical mirrors), rays farther from the principle axis do not remain parallel to the principle axis. Thus, the third assumption is not followed, and the focus gradually shifts towards the pole.
- The relation `("f" = "R"/2)` giving a single point focus is not followed, and the image does not converge at a single point, resulting in a distorted or defective image.
- This defect arises due to the spherical shape of the reflecting surface.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Two plane mirrors are inclined at angle of 40° between them. Number of images seen of a tiny object kept between them is ______.
Choose the correct option.
Which of the following aberrations will NOT occur for spherical mirrors?
Answer the following question.
What is focal power of a spherical mirror or a lens? What may be the reason for using P = `1/"f"` as its expression?
Answer the following question.
At which positions of the objects do spherical mirrors produce a diminished image?
At which positions of the objects do spherical mirrors produce a magnified image?
Solve Numerical example.
Estimate the number of images produced if a tiny object is kept in between two plane mirrors inclined at 35°, 36°, 40° and 45°.
Solve Numerical example.
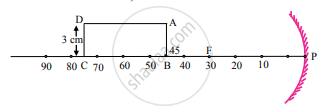
A rectangular sheet of length 30 cm and breadth 3 cm is kept on the principal axis of a concave mirror of focal length 30 cm. Draw the image formed by the mirror on the same diagram, as far as possible on scale.
A car uses a convex mirror of curvature 1.2 m as its rear-view mirror. A minibus of cross-section 2.2 m × 2.2 m is 6.6 m away from the mirror. Estimate the image size.
A 4.5 cm long needle is placed 10 cm away from a convex mirror of focal length 16 cm. Locate the image of the needle from the mirror.
Which of the following statements is incorrect?
As the position of an object (u) reflected from a concave mirror is varied, the position of the image (v) also varies. For the values of u from 0 to +`oo,` the graph between v versus u will be ______.
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is formed on the screen placed at distance v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between `1/"v"` versus `1/"u"` is (magnitude only).
An object is placed at a distance u from a concave mirror and its real image is formed on the screen placed at distance v from the mirror. If f is the focal length of the mirror, then the graph between `1/"v"` versus `1/"u"` is (magnitude only).
For convex mirrors, whatever may be the position of the object, the image formed is always on the ______.
A large glass slab `(µ = 5/3)` of thickness 8 cm is placed over a point source of light on a plane surface. It is seen that light emerges out of the top surface of the slab from a circular area of radius R cm. What is the value of R?
The lower half of a concave mirror is covered with Opaque material. Then ______.
