Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State the trends in the variation of electronegativity in groups and periods.
उत्तर
1. Variation of electronegativity in a group: The electronegativity decreases down a group. As we move down a group, the atomic radius increases, and the nuclear attractive force on the valence electron decreases. Hence electronegativity decreases in a group.
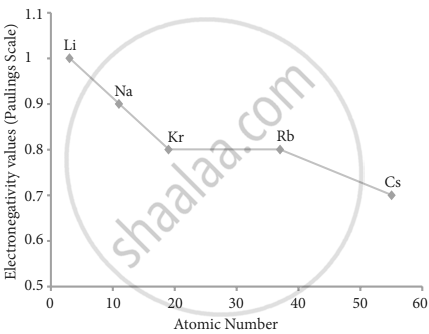
Variation of electronegativity along with I group
2. Variation of electron negativity in a period: The electronegativity increases across a period from left to right. Since the atomic radius decreases in a period, the attraction between the valence electron and the nucleus increases. Hence the tendency to attract shared pair of electrons increases. Therefore, electronegativity increases in a period.
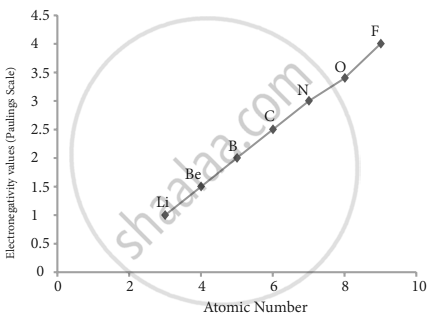
Variation of electronegativity along with II group
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which of the following is the second most electronegative element?
Which one of the following is true about metallic character when we move from left to right in a period and top to bottom in a group?
What is the effective nuclear charge?
Is the definition given below for ionisation enthalpy is correct?
"Ionisation enthalpy is defined as the energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from the valence shell of an atom"
Magnesium loses electrons successively to form Mg+, Mg2+ and Mg3+ ions. Which step will have the highest ionisation energy and why?
Energy of an electron in the ground state of the hydrogen atom is −2.18 × 10−18 J. Calculate the ionisation enthalpy of atomic hydrogen in terms of kJ mol−1.
Why the first ionisation enthalpy of sodium is lower than that of magnesium while its second ionisation enthalpy is higher than that of magnesium?
By using Pauling's method calculate the ionic radii of K+ and Cl− ions in the potassium chloride crystal. Given that `"d"_("K"^+) - "Cl"^-` = 3.14 Å
Explain the following, give an appropriate reason.
Ionisation potential of N is greater than that of O
What is the screening effect?
