Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
उत्तर १
| Convex lens | Concave lens | |
| 1. | A convex lens can form both real and virtual images | A concave lens always forms a virtual image |
| 2. | It can form a magnified image. | The image is always diminished in size. |
उत्तर २
1) A convex lens is thicker in the middle, while a concave lens is thinner in the middle.

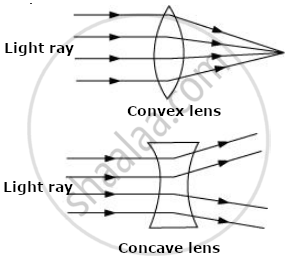
2) A convex lens converges the light ray falling on it, while a concave lens diverges the light ray falling on it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Suppose you have focused on a screen the image of candle flame placed at the farthest end of the laboratory table using a convex lens. If your teacher suggests you to focus the parallel rays of the sun, reaching your laboratory table, on the same screen, what you are expected to do is to move the:
(a) lens slightly towards the screen
(b) lens slightly away from the screen
(c) lens slightly towards the sun
(d) lens and screen both towards the sun
An image formed by a concave ______ cannot be obtained on a screen.
A concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Which type of lens forms always a virtual image?
Explain why, a stick half immersed in water appears to be bent at the surface. Draw a labelled diagram to illustrate your answer.
Write the new Cartesian sign convention for spherical lenses.
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
If a spherical lens has a power of, −0.25 D, the focal length of this lens will be :
(a) −4 cm
(b) −400 mm
(c) −4 m
(d) −40 cm
What are the three principal rays that are drawn to construct the ray diagram for the image formed by a lens? Draw diagrams to support your answer.
A convex lens forms an image of an object equal to the size of the object. Where is the object placed in front of the lens?
