Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suppose the gravity of the earth suddenly becomes zero, then in which direction will the moon begin to move if no other celestial body affects it?
उत्तर
The circular motion of the moon around the earth is due to the centripetal force provided by the gravitational force of the earth. Therefore,
when the gravity of the earth suddenly becomes zero, the moon will begin to move in a straight line in the direction in which it was moving at that instant. That is the moon will move along the tangent to the circular orbit at that instant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain why the value of g is zero at the centre of the earth.
The CGS unit of G is dyne.cm2/g2.
The value of G varies from place to place.
As we go above the earth's surface, value of g increases.
The mass of the moon is `1/81` of the mass of the earth. Its diameter is `1/3.7` of that of the earth. If acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2, then the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon.
The mass of a body on the surface of the earth is 10 kg. The mass of the same body on the surface on the moon is `"g"_"m" = 1/6 "g"_"e"`, where gm, ge acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon and the earth respectively.
The depth 'd' below the surface of the earth at which acceleration due to gravity becomes `(g/n)` is ______.
R = radius of the earth, 'g' = acceleration due to gravity, n = integer
A wire AB is carrying steady current 'I1' and is kept on the table. Another wire CD carrying current 'I2' is held parallel and directly above AB at a distance 'r'. When wire CD is left free and it remains suspended at its position, its mass per unit length is (g =acceleration due to gravity) ____________.
The force of attraction between two unit point masses separated by a unit distance is called
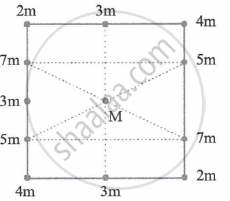
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.