Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The angle between the resultant contact force and the normal force exerted by a body on the other is called the angle of friction. Show that, if λ be the angle of friction and μ the coefficient of static friction λ ≤ tan−1 μ.
उत्तर
Let
f be the applied force,
R be the normal reaction force and
F be the frictional force.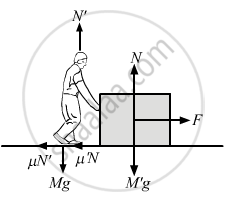
The coefficient of static friction is given by
`u = tanlambda = "F"/"R"`
(where λ is the angle of friction)
When F = μR, F is the limiting friction (maximum friction). When applied force increases and the body still remains still static then the force of friction increases up to its maximum value equal to limiting friction (μR).
F < μR
`thereforetanlambda="F"/"R"<=(muR)/R`
⇒ tan λ ≤ μ
⇒ λ ≤ tan−1 μ
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
In a situation the contact force by a rough horizontal surface on a body placed on it has constant magnitude. If the angle between this force and the vertical is decreased, the frictional force between the surface and the body will
A block A kept on an inclined surface just begins to slide if the inclination is 30°. The block is replaced by another block B and it is found that it just begins to slide if the inclination is 40°.
Let F, FN and f denote the magnitudes of the contact force, normal force and the friction exerted by one surface on the other kept in contact. If none of these is zero.
(a) F > FN
(b) F > f
(c) FN > f
(d) FN − f < F < FN + f.
The contact force exerted by a body A on another body B is equal to the normal force between the bodies We conclude that
(a) the surface must be frictionless
(b) the force of friction between the bodies is zero
(c) the magnitude of normal force equal that of friction
(d) the bodies may be rough but they don't slip on each other.
A block is placed on a rough floor and a horizontal force F is applied on it. The force of friction f by the floor on the block is measured for different values of F and a graph is plotted between them.
(a) The graph is a straight line of slope 45°.
(b) The graph is a straight line parallel to the F-axis.
(c) The graph is a straight line of slope 45° for small F and a straight line parallel to the F-axis for large F.
(d) There is a small kink on the graph.
A body slipping on a rough horizontal plane moves with a deceleration of 4.0 m/s2. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane?
Repeat part (a) of problem 6 if the push is applied horizontally and not parallel to the incline.
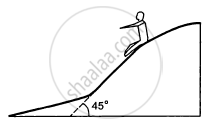
In a children-park an inclined plane is constructed with an angle of incline 45° in the middle part (in the following figure). Find the acceleration of boy sliding on it if the friction coefficient between the cloth of the boy and the incline is 0.6 and g = 19 m/s2.
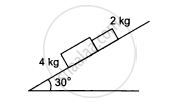
In the following figure shows two blocks in contact sliding down an inclined surface of inclination 30°. The friction coefficient between the block of mass 2.0 kg and the incline is μ1, and that between the block of mass 4.0 kg and incline is μ2. Calculate the acceleration of the 2.0 kg block if (a) μ1 = 0.20 and μ2 = 0.30, (b) μ1 = 0.30 and μ2 = 0.20. Take g = 10 m/s2.
Two masses M1 and M2 are connected by a light rod and the system is slipping down a rough incline of angle θ with the horizontal. The friction coefficient at both the contacts is μ. Find the acceleration of the system and the force by the rod on one of the blocks.
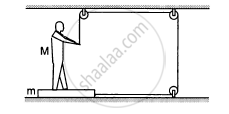
The friction coefficient between the board and the floor shown in the following figure is μ. Find the maximum force that the man can exert on the rope so that the board does not slip on the floor.
The friction coefficient between the two blocks shown in the following figure is μ but the floor is smooth. (a) What maximum horizontal force F can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium of the system? (b) Suppose the horizontal force applied is double of that found in part (a). Find the accelerations of the two masses.
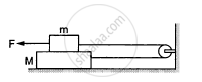
Consider the situation shown in the following figure. Suppose a small electric field E exists in the space in the vertically charge Q on its top surface. The friction coefficient between the two blocks is μ but the floor is smooth. What maximum horizontal force F can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium?
[Hint: The force on a charge Q bye the electric field E is F = QE in the direction of E.]
A block of mass 2 kg is pushed against a rough vertical wall with a force of 40 N, coefficient of static friction being 0.5. Another horizontal force of 15 N, is applied on the block in a direction parallel to the wall. Will the block move? If yes, in which direction? If no, find the frictional force exerted by the wall on the block.
A block placed on a rough horizontal surface is pulled by a horizontal force F. Let f be the force applied by the rough surface on the block. Plot a graph of f versus F.
The coefficient of static friction between a wooden block of mass 0.5 kg and a vertical rough wall is 0.2. The magnitude of horizontal force that should be applied on the block to keep it adhered to the wall will be ______ N. [g = 10 ms-2]
