Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The circuit diagram Fig shows three resistors 2 Ω, 4 Ω and R Ω connected to a battery of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 3 Ω. If main current of 0.25 A flows through the circuit, find:
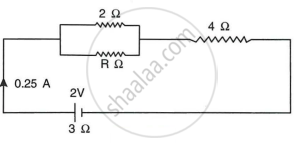
- the p.d. across the 4 Ω resistor,
- the p.d. across the internal resistance of the cell,
- the p.d. across the R Ω or 2 Ω resistors
- the value of R.
उत्तर
Current I = 0.25 A = `1/4` A,
(i) Potential difference across the 4Ω resistor = current through the resistor × its resistance
= 0.25 × 4
= 1V
(ii) Potential difference across internal resistance= current through internal resistance × internal resistance
= 0.25 × 3
= 0.75V
(iii) P.d. across the R Ω or 3 Ω resistor= emf - (p.d. across 4Ω resistor + p.d. across internal resistance)
= 2 - (1 + 0.75)
= 0.25V
(iv) We know, e = I `[("r" + 4 Ω) + (1/2 + 1/"R")^-1]`
2 = 0.25 `[7 + (2"R"/"R" + 2)]`
or, `(2"R")/("R" + 2) = 1`
or 2R = R + 2
or R = 2 Ω
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Differentiate between resistances in series and parallel.
With a neat labelled diagram and derive the equation for three resistances connected in parallel.
Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the combination has a resistance of 9 Ω.
The equivalent resistance of the parallel combination of two resistors of 60Ω and 40Ω is _______.
A) 24Ω
(B) 100Ω
(C) 50 Ω
(D) 240Ω
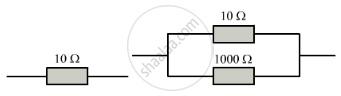
Which of the following arrangement, A or B, has the lower combined resistance?
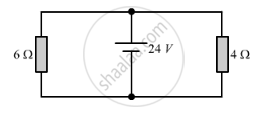
Find the current in each resistor in the circuit shown below:
Show with the help of diagrams, how you would connect three resistors each of resistance 6 Ω, so that the combination has resistance of (i) 9 Ω (ii) 4 Ω.
A resistor of 8 ohms is connected in parallel with another resistor X. The resultant resistance of the combination is 4.8 ohms. What is the value of the resistor X?
You are given three resistances of 1, 2 and 3 ohms. Shows by diagrams, how with the help of these resistances you can get:
(i) 6 Ω
(ii) `6/1` Ω
(iii) 1.5 Ω
How does the resistance of a metallic wire depend on the length of wire?
