Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
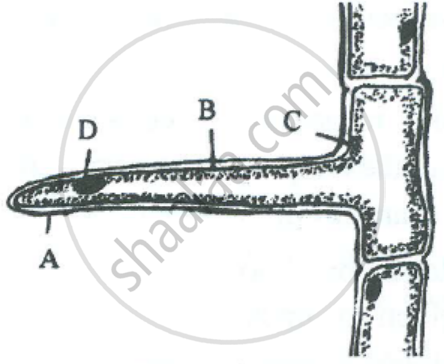
The diagram of an given below demonstrates a particular process in plants. Study the same and answer the questions that follow :

(i) Name the apparatus.
(ii) Which phenomenon is demonstrated by this apparatus?
(iii) Explain the phenomenon mentioned in (ii) above.
(iv) State two limitations of using this apparatus.
(v) What is the importance of the air bubble in the experiment?
(vi) Name the structures in a plant through which the above process takes place.
उत्तर
(i) The apparatus is called Ganong’s Potometer.
(ii) The phenomenon is called transpiration.
(iii) The evaporative loss of water in the form of water vapour from the aerial parts of plants is known as transpiration.
(iv) Two limitations are
- It is not easy to introduce the air bubble into the capillary.
- The twig may not remain fully alive for a long time.
(v) The air bubble helps measure the rate of transpiration.
(vi) Transpiration occurs through roots.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct answer:
Wilting of plants occurs when ____________
The diagram below represents a layer of epidermal cells showing a fully grown root hair. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow:
Mention one distinct difference between the parts labelled A and B.
What is toxicity ?
The below figure shows a root hair:
(i) Label the parts 1 to 4.
(ii) What is the role of part 4?
(iii) Why is the root hair one-celled?
(iv) What will happen to the root hair if some fertilizer is added to the soil near the root hair?
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Diffusion | (a) The exit or flow of water from the cell to the outer environment. |
| (ii) Xylem | (b) The shrinkage of protoplasm when the cell is kept in a hypertonic solution. |
| (iii) Root pressure | (c) The tissue through which water and mineral salts move upward in a plant. |
| (iv) Isotonic solution | (d) Two solutions which have equal osmotic pressure. |
| (v) Exosmosis | (e) The process by which the molecules of perfume spread in the room when the bottle is open. |
| (vi) Osmosis | (f) The process by which roots absorb water from the soil. |
| (vii) Plasmolysis | (g) The pressure by which water rises up to some feet in a lofty tree. |
| (viii) Hypotonic solution | (h) The concentration of the solution when lower than that of the cell sap. |
Plasma Membrane is ______.
Root hair is ________ extension of epiblema cells.
From which type of cells, root hair is originated
Epiphytic plants like orchids absorb water vapours from air with the help of epiphytic roots having special tissue called ____________.
Which of the following are the components of cell wall of root hair?
