Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
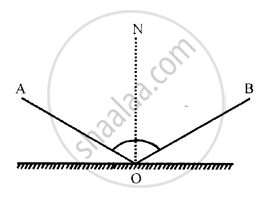
The diagram in Fig. shows an incident ray AO and the reflected ray OB from a plane mirror. The angle AOB is 30°. Draw normal on the plane mirror at the point O and find:
उत्तर
(i) the angle of incidence
(ii) the angle of reflection

ON is normal on the plane mirror at point O
ON is perpendicular on a plane mirror
Angle of incidence ∠i = ∠AON
and angle of reflection ∠r = ∠BON
Since, ∠i – ∠r
∠AOB = 30°
⇒ ∠AON + ∠BON = 30°
⇒∠i + ∠i – 30°
⇒ 2 ∠i = 30°
⇒ ∠i = 30 / 2 = 15°
∴ Angle of incidence = ∠i = 15°
and Angle of reflection ∠i = 15°
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
An optician while testing the eyes of a patient keeps a chart of letters 3 m behind the patient and asks him to see the letters on the image of chart formed in a plane mirror kept at distance 2 m in front of him. At what distance is the chart seen by the patient?
State two uses of a plane mirror.
An object is placed (i) asymmetrically (ii) symmetrically, between two plane mirrors inclined at an angle of 50°. Find the number of images formed.
Prove experimentally that images are formed as far behind in a plane mirror as the object is in front of it.
State the mirror formula for the formation of total number of images formed in two plane mirrors, held at an angle.
Calculate the number of images formed in two plane mirrors, when they are held at the angle of (i) 72° (ii) 36°.
Draw a neat two ray diagram for the formation of images in two plane mirrors, when mirrors are at right angles to each other.
Write down the letters of the word ‘POLEX’ as seen in a plane mirror, held parallel to the plane of this paper.
Select the correct option:
A ray of light is incident on a concave mirror. If it is parallel to principal axis, the reflected ray will:
Identify the following kind of beam of light.