Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field is zero when the angle between the wire and the direction of magnetic field is:
45°
60°
90°
180°
उत्तर
180°
The force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field is zero when a current-carrying conductor is parallel to the field.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Observe the following figure:

If the current in the coil A is changed, will some current be induced in the coil B? Explain.
State the form of magnetic field lines around a straight current-carrying conductor.
Fill in the following blank with suitable words:
For a current-carrying solenoid, the magnetic field is like that of a ...........
What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field?
If the current in a wire is flowing in the vertically downward direction and a magnetic field is applied from west to east, what is the direction of force in the wire?
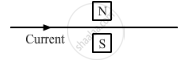
Which way does the wire in the diagram below tend to move?
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of a U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
When will coil come to rest?
The north pole of Earth’s magnet is in the ____________.
Which of the following factors affect the strength of force experience by current-carrying conduct in a uniform magnetic field?
|
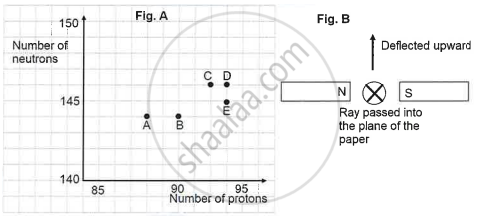
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.