Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
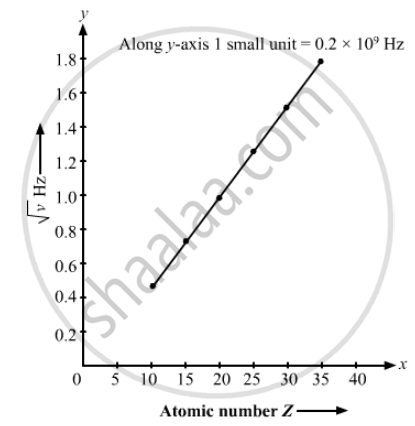
The Kβ X-rays from certain elements are given below. Draw a Moseley-type plot of √v versus Z for Kβ radiation.
| Element | Ne | P | Ca | Mn | Zn | Br |
| Energy (keV) | 0.858 | 2.14 | 4.02 | 6.51 | 9.57 | 13.3 |
उत्तर
We can directly get value of v by energy frequency relation.
hv = energy
Here, h = Planck's constant
`v = "Energy (in keV)"/h`
The required graph is as follows :
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the part of the electromagnetic spectrum which is:
produced by bombarding a metal target by high speed electrons.
To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does a wave of frequency 5 × 1019 Hz belong?
Name two electromagnetic waves of frequency smaller than that of violet light. State one use of each.
Name the rays or waves of highest frequency .
Name the waves produced by the changes in the nucleus of an atom.
An electromagnetic wave has a frequency of 500 MHz and a wavelength of 60 cm.name the medium through which it is travelling
When a Coolidge tube is operated for some time it becomes hot. Where does the heat come from?
The energy of a photon of a characteristic X-ray from a Coolidge tube comes from
If the potential difference applied to the tube is doubled and the separation between the filament and the target is also doubled, the cutoff wavelength
For harder X-rays,
(a) the wavelength is higher
(b) the intensity is higher
(c) the frequency is higher
(d) the photon energy is higher.
A free atom of iron emits Kα X-rays of energy 6.4 keV. Calculate the recoil kinetic energy of the atom. Mass of an iron atom = 9.3 × 10−26 kg.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
The stopping potential in a photoelectric experiment is linearly related to the inverse of the wavelength (1/λ) of the light falling on the cathode. The potential difference applied across an X-ray tube is linearly related to the inverse of the cutoff wavelength (1/λ) of the X-ray emitted. Show that the slopes of the lines in the two cases are equal and find its value.
(Use Planck constant h = 6.63 × 10-34 Js= 4.14 × 10-15 eVs, speed of light c = 3 × 108 m/s.)
Answer briefly.
What is a carrier wave?
The frequency of x-rays, y-rays and ultraviolet rays are respectively a, b and c. Then:-
Electromagnetic waves with wavelength
- λ1 is suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation.
- λ2 is used to kill germs in water purifiers.
- λ3 is used to improve visibility in runways during fog and mist conditions.
Identify and name the part of the electromagnetic spectrum to which these radiations belong. Also arrange these wavelengths in ascending order of their magnitude.
Arrange the following electromagnetic radiation in the ascending order of their frequencies:
X-rays, microwaves, gamma rays, radio waves
Write two uses of the following radiation.
Gamma rays
Which one of the following electromagnetic radiation has the least wavelength?
What is the speed of radio waves in vacuum?
What happens when an electron collides with a positron?
