Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The latitudinal extent of India is responsible for the variation in the climatic conditions which prevail in the country.
उत्तर
The Northern plains lie to north of the Tropic of Cancer in the Temperate Zone. The winters are much colder. South India lies below the Tropic of Cancer, in the tropics and gets the direct rays of the sun. Hence it is hot through most of the year. The winters are not so cold.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name a state that is the first to experience the onset of the monsoon.
Give geographical reasons for each of the following:
The Ganga Plains gets the monsoon rain much later than the west coast of India.
Study the climate data given below and answer the questions that follow:
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | June | July | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| Temperature in °C |
25.0 | 25.5 | 26.3 | 27.1 | 30.0 | 36.2 | 36.0 | 35.9 | 35.9 | 29.3 | 27.0 | 24.6 |
| Rainfall cm | 24.5 | 23.1 | 15.0 | 2.4 | 0.1 | 11.0 | 9.3 | 4.0 | 10.5 | 4.0 | 14.5 | 20.4 |
1) Calculate the annual temperature range.
2) What is the total annual rainfall?
3) Presuming that the station is located in India, give a reason for its location being on the east coast or west coast of India.
Give an account of weather conditions and characteristics of the cold season.
| Stations | Latitude | Altitude (Metres) | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May. | Jun. | July. | Aug. | Sep. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Annual Rainfall |
|
Temperature (°C) |
20.5 |
22.7 |
25.2 |
27.1 |
26.7 |
24.2 |
23.0 |
23.0 |
23.1 |
22.9 |
18.9 |
20.2 |
|||
| Bengaluru | 12°58'N | 909 |
|
|
|
||||||||||
| Rainfall (cm) | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 4.5 | 10.7 | 7.1 | 11.1 | 13.7 | 16.4 |
15.3 |
6.1 |
1.3 |
88.9 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
24.4 |
24.4 |
26.7 |
28.3 |
30.0 |
28.9 |
27.2 |
27.2 |
27.2 |
27.8 |
27.2 |
25.0 |
|||
|
Mumbai |
19° N | 11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
0.2 |
0.2 |
– |
– |
1.8 |
50.6 |
61.0 |
36.9 |
26.9 |
4.8 |
1.0 |
– |
183.4 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
19.6 |
22.0 |
27.1 |
30.1 |
30.4 |
29.9 |
28.9 |
28.7 |
28.9 |
27.6 |
23.4 |
19.7 |
|||
|
Kolkata |
22°34'N | 6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
1.2 |
2.8 |
3.4 |
5.1 |
13.4 |
29.0 |
33.1 |
33.4 |
25.3 |
12.7 |
2.7 |
0.4 |
162.5 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
14.4 |
16.7 |
23.3 |
30.0 |
33.3 |
33.3 |
30.0 |
29.4 |
28.9 |
25.6 |
19.4 |
15.6 |
|||
|
Delhi |
29° N | 219 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
2.5 |
1.5 |
1.3 |
1.0 |
1.8 |
7.4 |
19.3 |
17.8 |
11.9 |
1.3 |
0.2 |
1.0 |
67.0 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
16.8 |
19.2 |
26.6 |
29.8 |
33.3 |
33.9 |
31.3 |
29.0 |
20.1 |
27.0 |
20.1 |
14.9 |
|||
|
Jodhpur |
26°18'N | 224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
0.5 |
0.6 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
1.0 |
3.1 |
10.8 |
13.1 |
5.7 |
5.7 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
36.6 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
24.5 |
25.7 |
27.7 |
30.4 |
33.0 |
32..5 |
31.0 |
30.2 |
29.8 |
28.0 |
25.9 |
24.9 |
|||
|
Chennai |
13°4'N | 7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
4.6 |
1.3 |
1.3 |
1.8 |
3.8 |
22.2 |
8.7 |
11.3 |
11.9 |
30.6 |
35.0 |
0.2 |
128.6 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
21.5 |
23.9 |
28.3 |
32.7 |
35.5 |
32.0 |
27.7 |
27.3 |
27.9 |
26.7 |
23.1 |
20.7 |
|||
|
Nagpur |
21°9'N | 312 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
1.1 |
2.3 |
1.7 |
1.6 |
2.1 |
22.2 |
37.6 |
28.6 |
18.5 |
5.5 |
2.0 |
13.9 |
124.2 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
9.8 |
11.3 |
15.9 |
18.5 |
19.2 |
20.5 |
21.1 |
20.9 |
20.9 |
17.2 |
13.3 |
10.4 |
|||
|
Shillong |
24°34'N | 1461 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
1.4 |
2.9 |
5.6 |
14.6 |
29.5 |
47.6 |
35.9 |
34.3 |
30.2 |
18.8 |
3.8 |
1.0 |
225.3 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
26.7 |
27.3 |
28.3 |
28.7 |
28.6 |
26.6 |
26.2 |
26.2 |
26.5 |
26.7 |
26.6 |
26.5 |
|||
|
Thiruvananthapuram |
8°29'N | 61 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
2.3 |
2.1 |
3.7 |
10.6 |
20.8 |
35.6 |
22.3 |
14.6 |
13.8 |
27.3 |
20.6 |
7.5 |
181.2 | ||
|
Temperature (°C) |
−8.5 |
−7.2 |
−0.6 |
6.1 |
10.0 |
14.4 |
17.2 |
16.1 |
12.2 |
6.1 |
0.0 |
−5.6 |
|||
|
Leh |
34°N | 3506 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rainfall (cm) |
1.0 |
0.8 |
0.8 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.5 |
1.3 |
1.3 |
0.8 |
0.5 |
– |
0.5 |
8.5 |
In above Table the average mean monthly temperatures and amounts of rainfall of ten representative stations have been given. It is for you to study on your own and convert them into ‘temperature and rainfall’ graphs. A glance at these visual representations will help you to grasp instantly the similarities and differences between them. One such graph (Figure 1) is already prepared for you. See if you can arrive at some broad generalisations about our diverse climatic conditions. 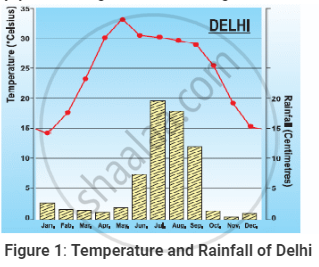
Re-arrange the ten stations in two different sequences:
(i) According to their distance from the equator.
(ii) According to their altitude above mean sea-level.
How are the sources of rainfall in the North-west part of India different from the rainfall experienced on the coastal areas of Eastern India in winter?
Patna receives heavier rain than Delhi.
Give reason why Shillong gets hardly 200 cm., rainfall during the year, whereas Cherrapunji gets more than 1250 cm, of rainfall although they are situated very close to each other.
Seventy-five percentage of Indian rainfall is from this wind.
