Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The neurons which carry impulse from the central nervous system to the muscle fibre.
पर्याय
afferent neurons
association neuron
efferent neuron
unipolar neuron
उत्तर
efferent neuron
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Receptor, Spinal cord, Effector, Motor neuron, Sensory neuron.
Name the following :
The layer of the eyeball that forms the transparent Cornea
The number of Spinal nerves in a human being are :
(A) 31 pairs
(B) 10 pairs
(C) 21 pairs
(D) 30 pairs
Mention the exact location of the Lacrimal gland
Fill in the blanks:
A neuron consists of ________ , _________ and ________.
Write the function of medullary sheath.
Rearrange the following in correct sequence pertaining to what is given within brackets at the end.
axon endings → nucleus → Dendrites → axon → perikaryon → Dendron(Neutron structure)
Nerve cells do not possess ______
A neuron contains all cell organelles except ______.
Classify neurons based on their structure.
Identify the INCORRECT statement regarding multipolar neuron.
Select the motor nerves from the following group.
Explain the function of the neuron.
Write one word for the following:
The kind of nerve carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Axons : Nerve :: Cytons : ______.
Name the following:
Three types of neurons
Define the following term:
Synaptic cleft
Give reason:
Neurotransmitters are broken down by an enzyme just after passing an impulse from one neuron to the other.
The figure given below is the basic structural and functional unit of the human nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
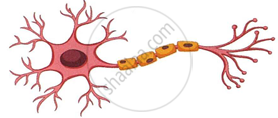 |
- Write the technical term for the diagram.
- Name two organs of our nervous system where these cells are richly found.
- How are these cells significant for us?
- Name the cell organelle that is absent in these cells and how does it affect our body metabolism?
- Redraw the same figure and label the following Perikaryon, Axon, Dendrites, Myelin sheath and Node of Ranvier.
