Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The radius of curvature of a convex mirror used as a rear view mirror in a moving car is 12.0 m. A truck is coming from behind it at a distance of 3.54 m. Calculate (a)
- position and
- size of the image relative to the size of the truck.
- What will be the nature of the image?
उत्तर
Given:
The mirror is convex.
Distance of the object from the mirror u = −3.54 cm
Radius of curvature of the mirror R = 12 cm
Focal length of the convex mirror f = 6 cm
a. We have to find the position of the image v and its magnification m.
Using the mirror formula, we get
`1/f = 1/v + 1/u`
⇒ `1/6 = 1/v + 1/-3.5`
⇒ `1/6 + (- 1)/3.54 = 1/v`
⇒ `1/v = 0.1667 - 0.2825`
⇒ `1/v = -0.1158`
⇒ `v = 1/-0.1158`
⇒ v ≈ −8.63 m
The position of the image is 8.63 m behind the mirror.
b. Now, using the magnification formula, we get
`M = v/u`
`M = (-8.63)/-3.54`
M = 0.244
c. Nature of the image
For a convex mirror:
- The image is virtual (formed behind the mirror).
- The image is diminished (smaller than the object).
- The image is erect (upright).
संबंधित प्रश्न
Which type of mirror has:
negative focal length?
State three characteristics of the image formed by a convex mirror.
Whatever be the position of the object, the image formed by a mirror is virtual, erect and smaller than the object. The mirror then must be:
(a) plane
(b) concave
(c) convex
(d) either concave or convex
A shop security mirror 5.0 m from certain items displayed in the shop produces on-tenth magnification.
What is the type of mirror?
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed:
between F1 and the optical centre O of the lens.
Which of the above two cases shows the use of convex lens as a magnifying glass? Give reasons for your choice.
An object is placed well outside the principal focus of a convex lens. Draw a ray diagram to show how the image is formed, and say whether the image is real or virtual.
An object is placed at the following distance from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm:
(a) 35 cm
(b) 30 cm
(c) 20 cm
(d) 10 cm
Which position of the object will produce:
(i) a magnified real image?
(ii) a magnified virtual image?
(iii) a diminished real image?
(iv) an image of same size as the object?
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
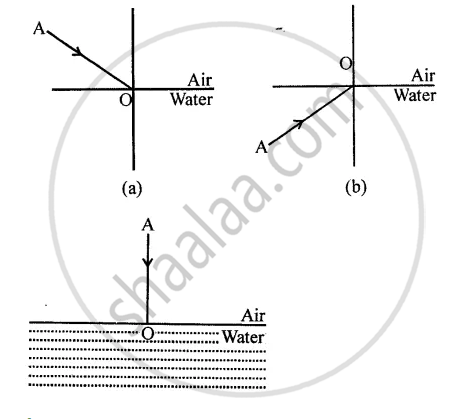
State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement.
The convex mirror always produces a virtual, diminished and erect image of the object.
If the object is at infinity in front of a convex mirror the image is formed at infinity.
