Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The refractive index of a material M1 changes by 0.014 and that of another material M2 changes by 0.024 as the colour of the light is changed from red to violet. Two thin prisms, one made of M1(A = 5.3°) and the other made of M2(A = 3.7°) are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. (a) Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination. (b) The prisms are now combined with their refracting angles similarly directed. Find the angular dispersion produced by the combination.
उत्तर
If μ'v and μ'r are the refractive indices of material M1, then we have:-
μ'v – μ'r = 0.014
If μv and μr are the refractive indices of material M2, then we have:-
μv – μr = 0.024
Now,
Angle of prism for M1, A' = 5.3°
Angle of prism for M2, A = 3.7°
(a) When the prisms are oppositely directed, angular dispersion (δ1) is given by
δ1 = (μv – μr)A – (μ'v – μ'r)A'
On substituting the values, we get:-
δ1 = 0.024 × 3.7° – 0.014 × 5.3°
= 0.0146°
So, the angular dispersion is 0.0146°.
(b) When the prisms are similarly directed, angular dispersion (δ2) is given by
δ2 = (μv – μr)A + (μ'v – μ'r)A'
On substituting the values, we get:-
δ2 = 0.024 × 3.7° + 0.014 × 5.3°
= 0.163°
So, the angular dispersion is 0.163°.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
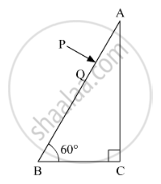
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC made of material of refractive index 1.5. Complete the path of ray through the prism. From which face will the ray emerge? Justify your answer.
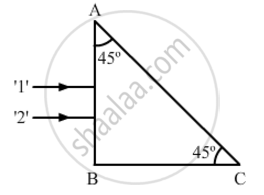
Two monochromatic rays of light are incident normally on the face AB of an isosceles right-angled prism ABC. The refractive indices of the glass prism for the two rays '1' and '2' are respectively 1.38 and 1.52. Trace the path of these rays after entering through the prism.
What is a dispersion of light
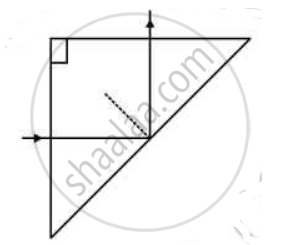
A ray of light incident normally on one face of a right isosceles prism is totally reflected, as shown in fig. What must be the minimum value of refractive index of glass? Give relevant calculations.
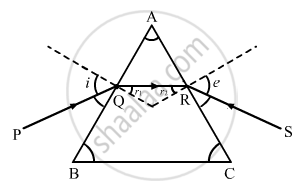
For any prism, prove that :
'n' or `mu = sin((A + delta_m)/2)/sin(A/2)`
where the terms have their usual meaning
Figure shows a ray of light passing through a prism. If the refracted ray QR is parallel to the base BC, show that (i) r1 = r2 = A/2 and (ii) angle of minimum deviation, Dm = 2i − A.
Give the formula that can be used to determine refractive index of materials of a prism in minimum deviation condition ?
The equation \[\omega = \frac{\mu_u - \mu_r}{\mu - 1}\] was derived for a prism having small refracting angle. Is it also valid for a prism of large refracting angle? Is it also valid for a glass slab or a glass sphere?
If three identical prisms are combined, is it possible to pass a beam that emerges undeviated? Undispersed?
A prism can produce a minimum deviation δ in a light beam. If three such prisms are combined, the minimum deviation that can be produced in this beam is _______________.
By properly combining two prisms made of different materials, it is possible to
(a) have dispersion without average deviation
(b) have deviation without dispersion
(c) have both dispersion and average deviation
(d) have neither dispersion nor average deviation
The minimum deviations suffered by, yellow and violet beams passing through an equilateral transparent prism are 38.4°, 38.7° and 39.2° respectively. Calculate the dispersive power of the medium.
Two prisms of identical geometrical shape are combined with their refracting angles oppositely directed. The materials of the prisms have refractive indices 1.52 and 1.62 for violet light. A violet ray is deviated by 1.0° when passes symmetrically through this combination. What is the angle of the prisms?
A thin prism of angle 6.0°, ω = 0.07 and μy = 1.50 is combined with another thin prism having ω = 0.08 and μy = 1.60. The combination produces no deviation in the mean ray. (a) Find the angle of the second prism. (b) Find the net angular dispersion produced by the combination when a beam of white light passes through it. (c) If the prisms are similarly directed, what will be the deviation in the mean ray? (d) Find the angular dispersion in the situation described in (c).
What is meant by the dispersive power of transparent material?
The refractive indices of material for red, violet and yellow colour light are 1.52, 1.62 and 1.59 respectively.
Calculate the dispersive power of the material. If the mean deviation is 40°. What will be the angular dispersion produced by a prism of this material?
