Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The speeds of red light and yellow light are exactly same
पर्याय
in vacuum but not in air
in air but not in vacuum
in vacuum as well as in air
neither in vacuum nor in air
उत्तर
in vacuum but not in air
Different wavelengths travel at different speeds through different media. In vacuum, the speeds of both the red light and yellow light are same but are different in air due to some optical density of air. Both wavelengths act in a different way in the air.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The speed of sound in air is 332 m s−1. Is it advisable to define the length 1 m as the distance travelled by sound in 1/332 s?
In Fizeau method of measuring the speed of light, the toothed wheel is placed in the focal plane of a converging lens. How would the experiment be affected if the wheel is slightly away from the focal plane?
In the original Fizeau method, the light travelled 8.6 km and then returned. What could be the difficulty if this distance is taken as 8.6 m?
What is the advantage of using a polygonal mirror with larger number of faces in Michelson method of measuring the speed of light?
Which of the following methods can be used to measure the speed of light in laboratory?
Which of the following methods can be used to measure the speed of light in water?
In an experiment to measure the speed of light by Fizeau's apparatus, following data are used: Distance between the mirrors = 12.0 km,
Number of teeth in the wheel = 180.
Find the minimum angular speed of the wheel for which the image is not seen.
In an experiment with Foucault's apparatus, the various distances used are as follows:
Distance between the rotating and the fixed mirror = 16 m
Distance between the lens and the rotating mirror = 6 m,
Distance between the source and the lens = 2 m.
When the mirror is rotated at a speed of 356 revolutions per second, the image shifts by 0.7 mm. Calculate the speed of light from these data.
In a Michelson experiment for measuring speed of light, the distance travelled by light between two reflections from the rotating mirror is 4.8 km. The rotating mirror has a shape of a regular octagon. At what minimum angular speed of the mirror (other than zero) the image is formed at the position where a nonrotating mirror forms it?
For light incident from air on a slab of refractive index 2, the maximum possible angle of refraction is ______.
If the velocity and wavelength of light in air is Va and λa and that in water is Va and λw, then the refractive index of water is ______.
An air bubble in glass slab of refractive index 1.5 (near normal incidence) is 5 cm deep when viewed from one surface and 3 cm deep when viewed from the opposite face. The thickness of the slab is,
A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of 80 cm. What is the area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out? Refractive index of water is 1.33. (Consider the bulb to be a point source.)
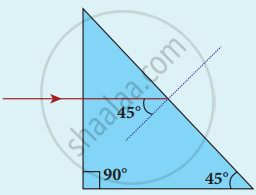
A beam of light consisting of red, green and blue is incident on a right-angled prism as shown in figure. The refractive index of the material of the prism for the above red, green and blue colours are 1.39, 1.44 and 1.47 respectively. What are the colours suffer total internal reflection?
A ray of light travels a distance of 12.0 m in a transparent sheet in 60 ns. The refractive index of the sheet is ______.
