Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The V − I characteristic of a silicon diode is as shown in the figure. Calculate the resistance of the diode at (i) I = 15 mA and (ii) V= −10 V.

उत्तर
(i) From the given curve, we have
voltage, V = 0.8 volt for current, I = 20 mA
voltage,V = 0.7 volt for current, I = 10 mA
\[\Rightarrow \Delta I = (20 - 10) mA = 10 \times {10}^{- 3} A\]
\[ \Rightarrow \Delta V = (0 . 8 - 0 . 7) = 0 . 1 V\]
\[ \therefore \text { Resistance, } R = \frac{\Delta V}{\Delta I}\]
\[ \Rightarrow R = \frac{0 . 1}{10 \times {10}^{- 3}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow R = 10 \Omega\]
(ii) \[For V = - 10 V, we have\]
\[ I = - 1 \mu A = 1 \times {10}^{- 6} A\]
\[ \Rightarrow R = \frac{10}{1 \times {10}^{- 6}} = 1 . 0 \times {10}^7 \Omega\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The forward characteristic curve of a junction diode is shown in Figure 4 below :
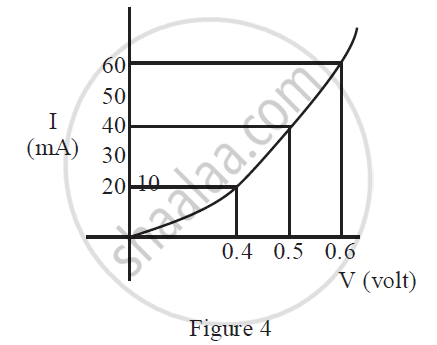
Calculate the resistance of the diode at
(1) V = 0.5 V
(2) I = 60 mA
Mark the correct options.
(a) A diode valve can be used as a rectifier.
(b) A triode valve can be used as a rectifier.
(c) A diode valve can be used as an amplifier.
(d) A triode valve can be used as an amplifier.
In semiconductor physics, what is the function of a rectifier?
