Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The V-I graph for a series combination and for a parallel combination of two resistors is shown in Fig – 8.38. Which of the two, A or B, represents the parallel combination? Give a reason for your answer.
उत्तर
For the same change in I, change in V is less for the straight line A than for the straight line B (i.e., the straight line A is less steeper than B), so the straight line A represents small resistance, while the straight line B represents more resistance. In parallel combination, the resistance decreases while in series combination, the resistance increases. So A represents the parallel combination.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below:
| I (amperes) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volts) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Define the unit of resistance (or Define the unit "ohm").
The potential difference between the terminals of an electric iron is 240 V and the current is 5.0 A. What is the resistance of the electric iron?
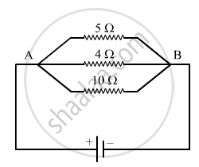
In the circuit diagram given below, the current flowing across 5 ohm resistor is 1 amp. Find the current flowing through the other two resistors.
Explain the analogy between the flow of charge (or current) in a conductor under a potential difference with the free fall of a body under gravity.
Calculate the current flowing through each of the resistors A and B in the circuit shown in the following figure.

Write an expression for the electrical power spent in flow of current through a conductor in terms of resistance and potential difference.
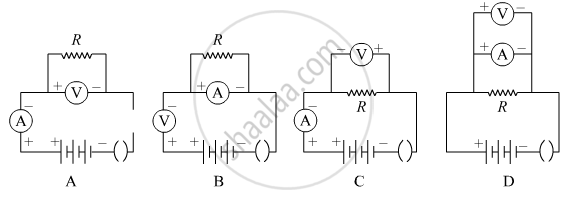
Which one of the following is the correct set-up for studying the dependence of the current on the potential difference across a resistor and why?
Find the potential difference required to flow a current of 300 mA in a wire of resistance 20 Ω.
