Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The velocity of a body moving in a straight line is increased by applying a constant force F, for some distance in the direction of the motion. Prove that the increase in the kinetic energy of the body is equal to the work done by the force on the body.
उत्तर
Let the body covers a distance s when a constant force F is applied in the direction of motion.
Work done by this force, W = F. s
Let the velocity of the object of mass m change
from u to v with acceleration and on application
of constant force F, then F = ma
From equation of motion, v2 − u2 = 2as, we get
s = `("v"^2 - "u"^2)/(2"a")`
∴ W = Fs = ma `(("v"^2 - "u"^2)/(2"a"))`
= `1/2 "mv"^2 - 1/2 "mu"^2`
= final kinetic energy – initial kinetic energy
= change in kinetic energy
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the energy changes in the following case while in use:
A ceiling fan
State the energy changes in the following while in use A loudspeaker .
State the energy changes that occur in the following :
An electric generator (or dynamo).
Energy can exist in several forms and may change from one form to another. State the energy changes that occur in the Charging of a battery.
State the energy changes in the following case while in use:
A solar cell
State the law of conservation of energy.
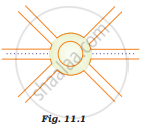
A boy is moving on a straight road against a frictional force of 5 N. After travelling a distance of 1.5 km he forgot the correct path at a roundabout (Fig. 11.1) of radius 100 m. However, he moves on the circular path for one and half-cycle and then he moves forward up to 2.0 km. Calculate the work done by him.
Can any object have momentum even if its mechanical energy is zero? Explain
Is it possible that an object is in a state of accelerated motion due to external force acting on it, but no work is being done by the force? Explain it with an example.
The energy conversion in a washing machine is from ______.
