Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The volume of air in the lungs and the rate at which it is exchanged during inspiration and expiration was measured.
The following diagram shows a group of the lung volumes and capacities.
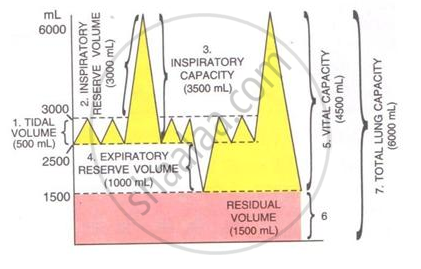
Study the diagram carefully and explain briefly the following :
Residual volume (RV)
उत्तर
Residual volume (RV): Air left in the lungs, even after forcible expiration is called residual volume. It is 1500 mL.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable diagram, describe the conducting system of the human heart.
Diffusion of gases occurs in the alveolar region only and not in the other parts of respiratory system. Why?
During respiration there is
Give Suitable Explanation for the Following :
Breathing through the nose is said to be healthier than through the mouth.
Starting from the nostrils, trace the path in sequence which the inspired air takes until it reaches the air sacs.
Name the gas which is expelled out during expiration. Where is it originally produced in our bodies?
Name the following:
Respiratory process in which oxygen is not utilized.
What factors are most likely to affect the breathing rate?
What do you understand by inhalation and exhalation? How are they different from each other?
Name the following:
High breathing rate.
Name the following:
No breathing.
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative from those given below.
The protective covering of the lung ______.
Alveoli provide the surface area for exchange of ______.
Which of the following is the structural and functional unit of pulmonary respiration?
The part where the exchange of gases occurs during respiration is:
Pick the odd one out from each of the groups given below on the basis of respiratory organs. Give a reason for your answer.
snake, tadpole, crow, goat
Match the following
| i. | Alveoli | a. | Yeast |
| ii. | Ethanol | b. | Gaseous exchange |
| iii. | Diffusion | c. | Amino acids |
| iv. | Protein | d. | Perfume |
For completion of respiration process, write the given steps in sequential manner
- Diffusion of gases (O2 and CO2) across alveolar membrane.
- Transport of gases by blood.
- Utilisation of O2 by the cells for catabolic reactions and resultant release of CO2.
- Pulmonary ventilation by which atmospheric air is drawn in and CO2 rich alveolar air is released out.
- Diffusion of O2 and CO2 between blood and tissues.
Name the lymphoid organ present in the human pharynx.
