Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two long straight parallel conductors carrying currents I1 and I2 are separated by a distance d. If the currents are flowing in the same direction, show how the magnetic field produced by one exerts an attractive force on the other. Obtain the expression for this force and hence define 1 ampere.
उत्तर
Fab = Force experienced by wire 'a' of length 'l' due to the magnetic field of wire 'b'
Fba = Force experienced by wire 'a' of length 'l' due to the magnetic field of wire 'b'
Ba = Magnetic field due to wire 'a'
Bb = Magnetic field due to wire 'b'
Ba = `(mu_0I_a)/(2rd)`
Since `vecF = i(vecl xx vecB)`
`F_(ba) = I_1. l(mu_0I_2)/(2rd)`
Similarly, `F(ab) = I_1.l(mu_0I_2)/(2rd)`
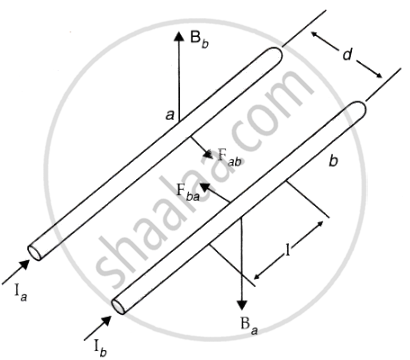
The direction of force experienced by wire 'a' is toward wire 'b'. (As shown in the diagram).
Similarly, the direction of force experienced by wire 'b' is toward wire 'a'. Thus, the force is attractive.
If two long wires are placed in a vacuum at a separation of 1 m, one Ampere would be defined as the current in each wire that would produce a force of 2 × 10–7Nm–1 per unit length of wire.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Derive the expression for force per unit length between two long straight parallel current carrying conductors. Hence define one ampere.
An electron beam projected along the positive x-axis deflects along the positive y-axis. If this deflection is caused by a magnetic field, what is the direction of the field? Can we conclude that the field is parallel to the z-axis?
A charged particle goes undeflected in a region containing an electric and a magnetic field. It is possible that
(a) `vecE" || "vecB , vecv" || " vec E `
(b) `vecE "is not parallel" vecB`
(c) `vecv " || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
(d) `vecE" || " vecB but vecv "is not parallel"`
A long, straight wire carries a current along the z-axis, One can find two points in the x−y plane such that
(a) the magnetic fields are equal
(b) the directions of the magnetic fields are the same
(c) the magnitudes of the magnetic fields are equal
(d) the field at one point is opposite to that at the other point.
A long, straight wire carrying a current of 1.0 A is placed horizontally in a uniform magnetic field B = 1.0 × 10−5 T pointing vertically upward figure. Find the magnitude of the resultant magnetic field at the points P and Q, both situated at a distance of 2.0 cm from the wire in the same horizontal plane.
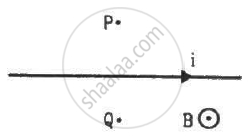
Figure shows two parallel wires separated by a distance of 4.0 cm and carrying equal currents of 10 A along opposite directions. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field B at the points A1, A2, A3.

Consider a 10-cm long piece of a wire which carries a current of 10 A. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the piece at a point which makes an equilateral triangle with the ends of the piece.
A long, straight wire carries a current i. Let B1 be the magnetic field at a point P at a distance d from the wire. Consider a section of length l of this wire such that the point P lies on a perpendicular bisector of the section B2 be the magnetic field at this point due to this second only. Find the value of d/l so that B2 differs from B1 by 1%.
Two parallel wires separated by a distance of 10 cm carry currents of 10 A and 40 A along the same direction. Where should a third current by placed so that it experiences no magnetic force?
The figure below are two long, parallel wires carrying current in the same direction such that I1 < I2.
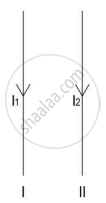
- In which direction will wire I1 move?
- If the direction of the current I2 is reversed, in which direction will the wire I1 move now?
