Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two polaroids P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other. Unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on P1. A third polaroid P3 is kept in between P1 and P2 such that its pass axis makes an angle of 60° with that of P1. Determine the intensity of light transmitted through P1, P2 and P3.
A narrow beam of unpolarised light of intensity I0 is incident on a polaroid P1. The light transmitted by it is then incident on a second polariod P2 with its pass axis making angle of 60° relative to the pass axis of P1. Find the intensity of the light transmitted by P2.
उत्तर
As given in the question the polaroid P1 and P2 are placed with their pass axes perpendicular to each other and polaroid P3 placed at 60°with repect to P1.
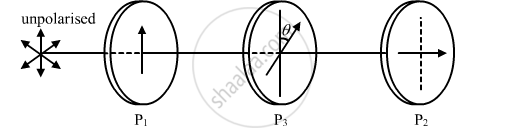
Therefore,
Intensity of light after falling on first polaroid P1, `I'=I_0/2`
Intensity of light after falling on third polaroid P3
`I'' = I'cos^2(theta)=I_0/2cos^2(60^@)=I_0/8`
Therefore the intensity `I_0/8` will pass through the P3 and angle between P3 and P2 is 30°. because of the condition given in the question.
Intensity of light after falling on second polaroid P2 =
`I'''= I'' cos^2(theta)=I_0/8cos^2(30^@) = (3I_0)/32`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
If the critical angle of a medium is sin-1(3/5), find the polarising angle.
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed polaroids. In which position of the polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum?
A beam of unpolarised light is incident on a glass-air interface. Show, using a suitable ray diagram, that light reflected from the interface is totally polarised, when μ = tan iB, where μ is the refractive index of glass with respect to air and iB is the Brewster's angle.
Show using a proper diagram how unpolarised light can be linearly polarised by reflection from a transparent glass surface.
Unpolarised light is incident on a polaroid. How would the intensity of transmitted light change when the polaroid is rotated?
A ray of light is incident on a transparent medium at a polarizing angle. What is the angle between the reflected ray and the refracted ray?
A ray of ordinary light is travelling in air. It is incident on air glass pair at a polarising angle of 56°. Find the angle of refraction in glass.
Mention the types of optically active crystals with example.
How is polarisation of light obtained by scattering of light?
What is normal focusing?
