Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two prisms ABC and DBC are arranged as shown in the figure.

The critical angles for the two prisms with respect to air are 41.1° and 45° respectively. Trace the path of the ray through the combination.
उत्तर
The ray incident normally at M enters undeviated.
At E, the angle of incidence is 45°. It is greater than the critical angle. So, it is totally internally reflected.

At H, the ray is incident normally. So it enters prism BDC undeviated.
At F, the angle of incidence is 60°. It is greater than the critical angle. So, it is internally reflected.
At G, the ray is incident normally. So, it comes out from the prism undeviated.
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does the angle of minimum deviation of a glass prism vary, if the incident violet light is replaced by red light? Give reason.
Trace the path of the ray (P) of light passing through the glass prism as shown in the figure. The prism is made of glass with critical angle ic = 41°.
Can you ever have a situation in which a light ray goes undeviated through a prism?
A flint glass prism and a crown glass prism are to be combined in such a way that the deviation of the mean ray is zero. The refractive index of flint and crown glasses for the mean ray are 1.620 and 1.518 respectively. If the refracting angle of the flint prism is 6.0°, what would be the refracting angle of the crown prism?
A small object is embedded in a glass sphere (μ = 1.5) of radius 5.0 cm at a distance 1.5 cm left to the centre. Locate the image of the object as seen by an observer standing (a) to the left of the sphere and (b) to the right of the sphere.
For a glass prism `(µ = sqrt(3))` the angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. Find the angle of the prism.
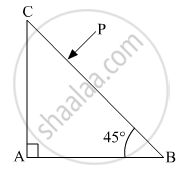
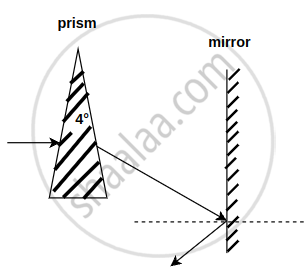
A horizontal ray of light passes through a prism of index 1.50 and apex angle 4° and then strikes a vertical mirror, as shown in the figure (a). Through what angle must the mirror be rotated if after reflection the ray is to be horizontal?
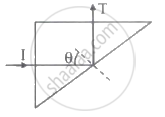
A triangular prism of glass is shown in the figure. A ray incident normally to one face is totally internally reflected. If θ is 45°, then the index of refraction of the glass is ______.
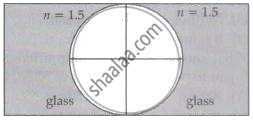
Two concave refracting surfaces of equal radii of curvature face each other in the air as shown in the figure. The point object O is placed midway between the centre and one of the poles. Then the separation between the images of O formed by each refracting surface is ______.
A ray of monochromatic light passes through an equilateral glass prism in such a way that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of emergence and each of these angles is 3/4 times the angle of the prism. Determine the angle of deviation and the refractive index of the glass prism.
