Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two sets A and B of four bulbs each are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow. Explain the difference in the two sets.
उत्तर १
In set A, the bulbs are connected in series. Thus, when the fuse of one bulb blows off, the circuit gets broken and current does not flow through the other bulbs also. In set B, the bulbs are connected in parallel. Thus, each bulb gets connected to its voltage rating (= 220 V) and even when the fuse of one bulb blows off, others remain unaffected and continue to glow.
उत्तर २
If the first bulb in set A were to blow a fuse and cut off power to the other three, none of the lights would work. All four bulbs in set B connect in a parallel. Bulbs keep glowing even after a single bulb blows.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Identify the following wires used in a household circuit: The wire is also called as the phase wire.
State the function of the following in a house circuiting kWh meter.
In what unit does the electric meter in a house measure the electrical energy consumed? What is its value in S.I unit?
Where is the main fuse in a house circuit connected?
The electric meter in a house records the consumption of ______.
In following figure shows three bulbs A, B and C each of rating 100 W, 220 V connected to the mains of 220 V. Answer the following:
- How is the bulb A connected with the mains? At what voltage does it glow?
- How are the bulbs B and C connected with the mains? At what voltage does the bulb B glow?
- How is the glow of bulbs A and C affected if bulb B gets fused?
- How is the glow of bulbs B and C affected if bulb A gets fused?
Which electrical component protects the electric circuit in case of excess current and which can also be used as a switch?
Name the wire to which this electrical component is connected in an electric circuit.
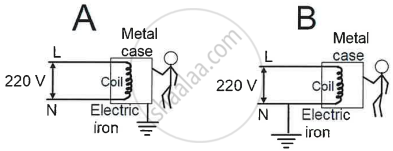
If live wire makes an accidental contact with the metal case, which circuit (A or B) in the diagram, illustrating an electric iron, is considered safe for the user (Assuming the fuse is present in the live wire in both circuits)? Justify your answer.
Two sets A and B each of four bulbs are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow. Which set of arrangement is preferred in housing circuit and why?
