Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Using graphs, explain any four types of elasticity of supply.
उत्तर
- Perfectly Inelastic Supply: If there is no change in quantity supplied with changes in the price of the product, then the supply of that commodity becomes perfectly inelastic (i.e., Es = 0) The supply curve will be a vertical line. This refers to when only one quantity can be supplied at any given price. The shape of perfectly inelastic supply is shown below.
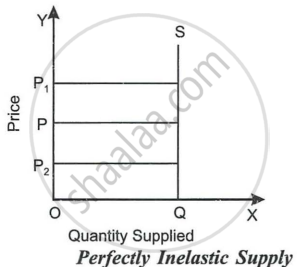
The figure clearly shows that quantity supplied is fixed at OQ, whatever the price (P, P1 or P2) . It cannot be increased or decreased at all. At all points on such a straight-line supply curve, the price elasticity of supply will be zero. - Perfectly Elastic Supply: When the supply of a commodity changes without change in its price, the supply of the commodity changes without change in its price and the supply of the commodity will be called perfectly elastic. The value of price elasticity of supply in this case is infinity, es = ∞. It is purely an imaginary concept and can only be explained with the help of an imaginary supply schedule as given below.
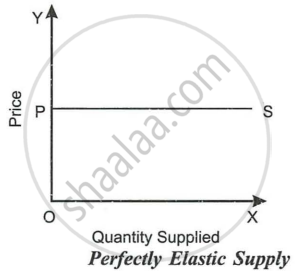
Perfectly elastic supply is shown graphically in. PS is the perfectly elastic supply curve, which is a horizontal line. It shows that at OP price, any quantity of the commodity can be supplied. Elasticity of supply will be infinite at all points on such a supply curve. - Relatively Elastic Supply: The supply of a commodity will be said to be elastic if the percentage change in quantity supplied exceeds the percentage change in price. In other words, elastic supply is one in which elasticity is greater than one, indicating high responsiveness in supply to change in price. In such a case, a straight line supply curve meets the Y-axis above the point of origin, as shown in Fig. At all points on the supply curve, price elasticity will be greater than one.
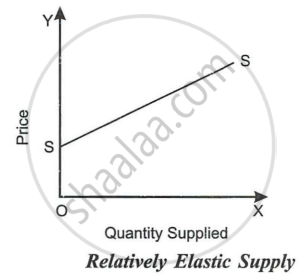
- Relatively Inelastic or Less than Unit Elastic: The supply of a commodity will be said to be inelastic if the percentage change in quantity supplied is less than the percentage change in price. For example, if the price of a good fall by 25% and supply decreases by only 5%, supply is said to be elastic
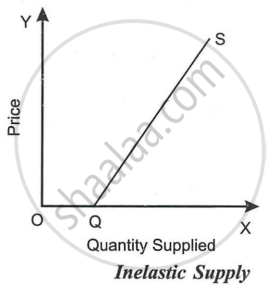
The Fig. shows inelastic supply. In the case of elastic supply, the supply curve meets the X-axis when extended to the right of the origin point. At all points of such a straight line supply curve, the elasticity of supply will be less than one.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
With the help of a suitable diagram, explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Es = ∞
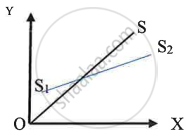
Identify the value of elasticity of supply for the supply curve OS and S1S2.
Identify the correct sequence of alternatives given in Column II by matching them with respective terms in Column:
| Column I | Column II |
| A. Perfectly Inelastic | (i) Es > 1 |
| B. Perfectly Elastic | (ii) Es < 1 |
| C. Inelastic | (iii) Es = 0 |
| D. Highly Elastic | (iv) Es = infinity |
Choose the correct alternative:
Draw a straight line supply showing elasticity greater than one.
Price of a product increases by 2%. As a result, its supply rises by 4%. What is elasticity of supply of the commodity?
The coefficient of elasticity of a commodity is 0.4. What percentage change in supply will take place if its price rises 20%?
If the price of a commodity increases by 50% and its supply increases by 25% then calculate the price elasticity of supply following the percentage method. Identify the degree of price elasticity.
Draw and explain the following degree of elasticity of supply.
Ep > 1
If the price of a commodity falls by 10% and consequently, the quantity supplied decreases by 20%, what will be its elasticity of supply?
Draw relatively inelastic supply.
