Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
We can see the sun even when it is little below the horizon because of ______.
पर्याय
Reflection of light
Refraction of light
Dispersion of light
Absorption of light
उत्तर
We can see the Sun even when it is little below the horizon because of refraction of light.
Explanation:
We can see the Sun even when it is a little below the horizon because of atmospheric refraction. The Earth’s atmosphere bends the light from the Sun upwards towards the eye of the observer. Even though the Sun itself might be just below the horizon line, the light is refracted or bent by the atmosphere, thus making the Sun appear to be visible.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the following blank with a suitable word:
When light is reflected, the angles of incidence and reflection are ............ .
Write the word AMBULANCE as it would appear when reflected in a plane mirror. Why is it sometimes written in this way (as its mirror image) on the front of an ambulance?
A boy with a mouth 5 cm wide stands 2 m away from a plane mirror. Where is his image and how wide is the image of his mouth?
The boy walks towards the mirror at a speed of 1 m/s. At what speed does his image approach him?
An extended object in the form of an arrow pointing upward has been placed in front of a plane mirror. Draw a labelled ray-diagram to show the formation of its image.
The image in a plane mirror is virtual and laterally inverted. What does this statement mean?
The image formed by a plane mirror is :
(a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged.
(b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
(c) real, at the surface of the mirror and enlarged.
(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.
Explain how to read the following message which was found on some blotting paper:
A ray of light travelling in glass emerges into air. State whether it will bend towards the normal or away from the normal.
A ray of light passes from air into a block of glass. Does it bend towards the normal or away from it?
In which material do you think light rays travel faster-glass or air?
Why does a ray of light bend when it travels from one medium to another?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Light travelling along a normal is ...............refracted.
Name the phenomenon due to which a pencil partly immersed in water and held obliquely appears to be bent at the water surface.
With the help of a diagram, show how when light falls obliquely on the side of a rectangular glass slab, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray.
Show the lateral displacement of the ray on the diagram.
Explain with the help of a labelled ray diagram, why a pencil partly immersed in water appears to be bent at the water surface. State whether the bending of pencil will increase or decrease if water is replaced by another liquid which is optically more dense than water. Give reason for your answer.
Light travelling from a denser medium to a rarer medium along a normal to the boundary:
(a) is refracted towards the normal
(b) is refracted away from the normal
(c) goes along the boundary
(d) is not refracted
A ray of light passes from a medium X to another medium Y. No refraction of light occurs if the ray of light hits the boundary of medium Y at an angle of:
(a) 0°
(b) 45°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
Image is formed by a mirror due to refraction of light.
Match the Following
| Column A | Column B |
| (a) white Light | (1) Convex mirror |
| (b) Refraction | (2) Concave mirror |
| (c) Virtual images | (3) refraction |
| (d) Real images | (4) spectrum |
| (e) Prism | (5) ray of light from glass to air |
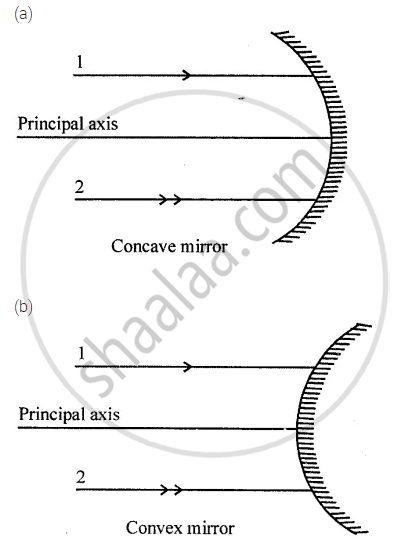
The diagram (figure) given below shows two parallel rays 1 and 2 incident on (a) a concave mirror, (b) a convex mirror. Draw the reflected rays and mark the focus by the symbol F.
What is the cause of refraction of light when it passes from one medium to another?
Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Explain how the formation of a rainbow occurs.
The laws of reflection hold true for:
Due to _______ pencil looks bent in water, in the given experiment.

Light changes its direction when going from one transparent medium to another transparent medium. This is called _______.
Observe the given figure and name the following.
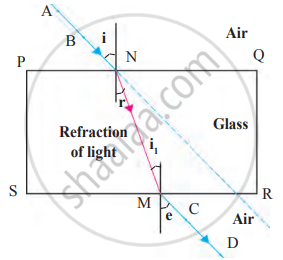
| Ray AB | |
| Ray NM | |
| Ray MD | |
| ∠ r |
Noor, a young student, was trying to demonstrate some properties of light in her Science project work. She kept ‘X’ inside the box (as shown in the figure) and with the help of a laser pointer made light rays pass through the holes on one side of the box. She had a small butter-paper screen to see the spots of light being cast as they emerged.
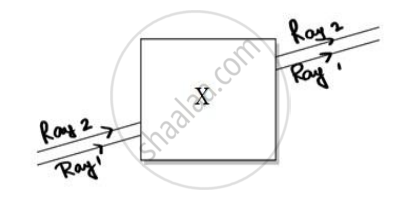
Her friend noted the following observations from this demonstration:
- Glass is optically rarer than air.
- Air and glass allow light to pass through them with the same velocity.
- Air is optically rarer than glass.
- Speed of light through a denser medium is faster than that of a rarer medium.
- The ratio: sin of angle of incidence in the first medium to the ratio of sin of angle of refraction in the second medium, gives the refractive index of the second material with respect to the first one.
Which one of the combinations of the above statements given below is correct.
Which object use the reflection of light?
Light travels fastest in a vacuum. Why?
A ray of light traveling in medium 1 strikes and travels into another transparent medium 2. If the speed of light is greater in medium 1, the ray will ______.
A star appears twinkling into the sky because of the reflection of light by the atmosphere.
Which is optically denser out of the two medium M1& M2 having the refractive indices = 1.71 and 1.36 respectively?
Match the following:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| 1. | r > 90 | a. | Light gazes at the surface of separation between the two modes. |
| 2. | r = 90 | b. | No refraction. |
| 3. | r < 90 | c. | Refracted ray away from the normal |
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are ______.
