Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What are α and β parameters for a transistor? Obtain a relation between them.
उत्तर
Alpha (αdc): It is defined as the ratio of collector current to emitter current.
`alpha_(dc)="I"_c/"I"_E` -----------------(Equation 1)
Beta (βdc): It is the current gain defined as the ratio of collector current to the base current.
`beta_(dc)="I"_c/"I"_B` --------------------(Equation 2)
Relation between αdc and βdc:
For a transistor,
IE = IB + IC (with Ic ≅ IE) -----------(Equation 3)
Divinding both the side of eqn.(3) with Ic ,we get :
`"I"_E/"I"_c="I"_B/"I"_C+1`
`1/alpha_(dc)=1/beta_(dc)+1`
`alpha_(dc)=beta_(dc)/(1+beta_(dc))` -----------------------(Equation 4)
Or, `beta_(dc)=alpha_(dc)/(1-alpha_(dc))` ----------------------(Equation 5)
Equations (4) and (5) give the relation between αdc and βdc of a transistor.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Write clearly, why in the case of a transistor (i) the base is thin and lightly doped
Write clearly, why in the case of a transistor (ii) the emitter is heavily doped.
Differentiate between three segments of a transistor on the basis of their size and level of doping.
How is a transistor biased to be in active state?
When a p-n-p transistor is operated in saturation region, then its ______.
(A) base-emitter junction is forward biased and base-collector junction is reverse biased.
(B) both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are reverse biased.
(C) both base-emitter and base-collector junctions are forward biased.
(D) base-emitter junction is reverse biased and base-collector junction is forward biased
Write the functions of the three segments of a transistor.
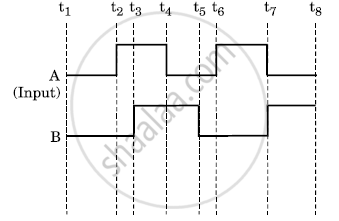
The figure shows the input waveforms A and B for ‘AND’ gate. Draw the output waveform and write the truth table for this logic gate.
Draw a typical input and output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Show how these characteristics can be used to determine (a) the input resistance (r1), and (b) current amplification factor (β)
Draw typical output characteristics of an n-p-n transistor in CE configuration. Show how these characteristics can be used to determine output resistance.
The output characteristic curve of a transistor at constant input current is plotted between
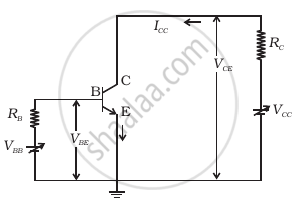
Consider the circuit arrangement shown in figure (a) for studying input and output characteristics of npn transistor in CE configuration.
 (a) |
 (b) |
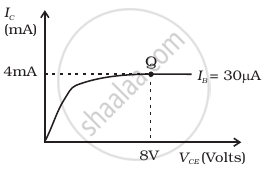
Select the values of RB and RC for a transistor whose VBE = 0.7 V, so that the transistor is operating at point Q as shown in the characteristics shown in figure (b). Given that the input impedance of the transistor is very small and VCC = VBB = 16 V, also find the voltage gain and power gain of the circuit making appropriate assumptions.
If an emitter current is changed by 4 mA, the collector current changes by 3.5 mA. The value of β will be ______.
Sanya performed an experiment of obtaining characteristic curves of a junction diode. When she forward biased it, she found that beyond forward voltage V = Vk, the conductivity is very high. When she reverse biased the diode she found that a very small current (of about a few microamperes) flows in the diode. It remained constant even though she varied the voltage.
(i) In Figure 1 below, which one of the diodes is forward biased?
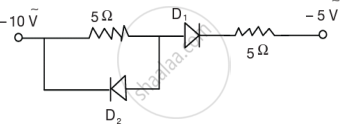
Figure 1
(ii) What is meant by a saturation current?
(iii) When applied voltage during forward bias is small, why does no current flow in the diode?
(iv) The circuit shown in Figure 2 below contains two diodes, each with a forward resistance of 50 Ω and with infinite resistance during reverse bias. If the battery voltage is 6V, then calculate the current through the 100 Ω resistance.
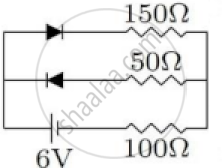
Figure 2
