Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the difference between cathode rays and beta rays? When the two are travelling in space, can you make out which is the cathode ray and which is the beta ray?
उत्तर
Cathode rays consist of electrons that are accelerated using electrodes. They do not carry high energy and do not harm human body. On the other hand, beta rays consist of highly energetic electrons that can even penetrate and damage human cells. Beta rays are produced by the decay of radioactive nuclei. If the two are travelling in space, they can be distinguished by the phenomenon named production of Bremsstrahlung radiation, which is produced by the deceleration of a high energy particle when deflected by another charged particle, leading to the emission of blue light. Only beta rays are capable of producing it.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Consider the D−T reaction (deuterium−tritium fusion)
\[\ce{^2_1H + ^3_1H -> ^4_2He + n}\]
Calculate the energy released in MeV in this reaction from the data:
`"m"(""_1^2"H")`= 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")`= 3.016049 u
Consider the D−T reaction (deuterium−tritium fusion)
\[\ce{^2_1H + ^3_1H -> ^4_2He}\]
Consider the radius of both deuterium and tritium to be approximately 2.0 fm. What is the kinetic energy needed to overcome the coulomb repulsion between the two nuclei? To what temperature must the gas be heated to initiate the reaction? (Hint: Kinetic energy required for one fusion event =average thermal kinetic energy available with the interacting particles = 2(3kT/2); k = Boltzman’s constant, T = absolute temperature.)
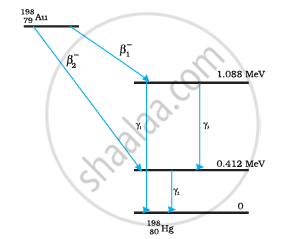
Obtain the maximum kinetic energy of β-particles, and the radiation frequencies of γdecays in the decay scheme shown in Fig. 13.6. You are given that
m (198Au) = 197.968233 u
m (198Hg) =197.966760 u
Write the basic nuclear process underlying β+ and β– decays.
Write the β-decay of tritium in symbolic form.
Write the basic nuclear process of neutron undergoing β-decay.
Why is the detection of neutrinos found very difficult?
In beta decay, an electron (or a positron) is emitted by a nucleus. Does the remaining atom get oppositely charged?
Ten grams of 57Co kept in an open container beta-decays with a half-life of 270 days. The weight of the material inside the container after 540 days will be very nearly
Consider a sample of a pure beta-active material.
A free neutron beta-decays to a proton with a half-life of 14 minutes. (a) What is the decay constant? (b) Find the energy liberated in the process.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
Complete the following decay schemes.
(a) `"" _88^226Ra → alpha+`
(b) `""_8^19O → _9^19F+`
(c) `""_13^25Al → ""_12^25Mg+`
