Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What does PCR stand for? Describe the different steps of PCR
उत्तर
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction:
Basic requirements for PCR technique are :
1) A DNA segment (100-35, 000 bp in length) be amplified.
2) Primers (forward and reverse) which are synthetic oligonucleotides of 17-30 nucleotide. They
are complementary to the sequence present on the desired DNA segment.
3) Four types of deoxyribonucleotides (dATP, dCTP, dGTP, dTTP). They are collectively called
dNTPs
4)A thermostable DNA polymerase, that can withstand up to 94°C. Usually, Taq polymerase isolated from bacterium Thermus aquaticus is used.
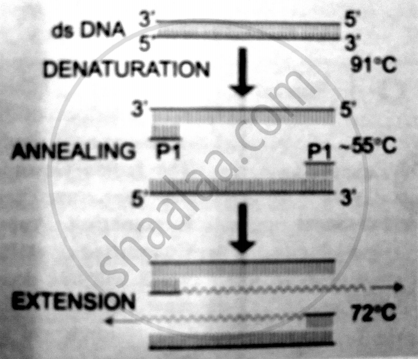
The three essential steps for PCR technique are :
1) Heat denaturation: This step involves heating of DNA at about 91°C. The heating breaks the hydrogen bonds to make ssDNA. The DNA molecule with more G-C pairs needs the higher
temperature.
2)Annealing: It is pairing of primers to the ssDNA segment. The primer has to be designed as per the requirement. this step requires temperature at about 55°C.
3) Polymerisation: The temperature is raised to 72°C. The Taq polymerase adds dNTPs behind
the primer on the ssDNA
These three steps constitute one cycle of the reaction. The process is carried out for about 28-30 cycles beyond which its reliability decreases.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Expand the following abbreviation: BAC
What is the cell that receives a recombinant gene called?
Explain the properties of a good or ideal cloning vector for rDNA technology.
Vectors are ____________ molecules that carry a foreign gene and replicate inside the host cell.
For which of the following reason Agrobacterium tumefaciens is most widely used for gene transfer in plants?
Which of the following is an INCORRECT match?
Which of the following is the right combination of primers in a PCR to amplify the DNA product?
Identify the CORRECT order of steps in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
What is the significance of adding proteases at the time of isolation of genetic material (DNA)?
What is EcoRI?
