Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the energy liberated during respiration?
उत्तर
The energy liberated during respiration is utilised for carrying out various life processes.
Some of the energy liberated during the breakdown of 03 the glucose molecule, is in the form of heat, but a large part of it is converted into chemical energy called Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP). Any activity inside the cell is carried out by the energy released by these ATP molecules.
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the following:
An organism which respires throughout life anaerobically.
Name the following:
Aerobic respiration requires_________ .
Why is it usually difficult to demonstrate respiration in green plants?
Fill in the blank:
_____________ is a chemical which absorbs oxygen of the air.
How do the following structures help in respiration in plants?
Lenticels _____________
How do the following structures help in respiration in plants?
Root hairs ____________
The following diagram refers to an apparatus which is used to demonstrate a physiological process:
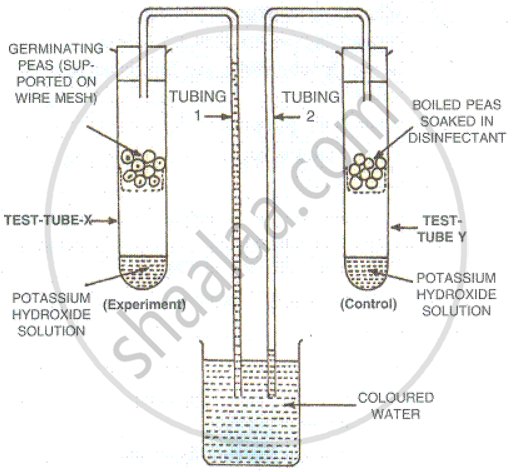
Define the biological process shown in the experiment.
What do you understand by respiration?
Name the following:
The process of living beings which is concerned with the release of energy for use in the body.
The roots of a plant take up oxygen from the ______ trapped between the ________ particles.
Which gas present in the air is essential for aerobic respiration? What is the role of oxygen during respiration?
A food stall owner was preparing dough for making bhaturas. He added a pinch of yeast and sugar to the dough and left it in a warm place. After a few hours, the dough had risen. There was a sour smell too.
Why did the dough smell sour?
Mitochondria are called powerhouses of the cell. Which of the following observations support this statement?
Explain the term “Energy Currency”. Which substance acts as energy currency in plants and animals?
If a person is feeling dizzy, glucose or fruit juice is given immediately but not a cheese sandwich Explain.
Respiration requires O2. How did the first cells on the earth manage to survive in an atmosphere that lacked O2?
RuBP carboxylase, PEP carboxylase, Pyruvate dehydrogenase, ATPase, cytochrome oxidase, Hexokinase, Lactate dehydrogenase.
Select/choose enzymes from the list above which are involved in
- Photosynthesis
- Respiration
- Both in photosynthesis and respiration
