Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the force between two objects, if the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
उत्तर
If the distance between the two objects is doubled, then
F'' = `(Gm_1m_2)/(2R^2)`
= `1/4 xx (Gm_1m_2)/(R^2)`
= `1/4` F
= `F/4`
Thus, the gravitational force between the two objects becomes one-fourth.
If the distance between the two objects is tripled, then
F′′′ = `(Gm_1m_2)/(3R)^2`
= `1/9 xx (Gm_1m_2)/R^2`
= `1/9 xx F`
= `F/9`
Thus, the gravitational force between the two objects becomes one-ninth.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Choose the correct answer from among the given ones:
For the problem 8.10, the direction of the gravitational intensity at an arbitrary point P is indicated by the arrow (i) d, (ii) e, (iii) f, (iv) g.
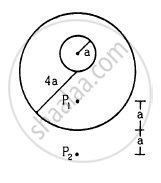
A uniform metal sphere of radius a and mass M is surrounded by a thin uniform spherical shell of equal mass and radius 4a (In the following figure). The centre of the shell falls on the surface of the inner sphere. Find the gravitational field at the points P1 and P2 shown in the figure.
How will the force of gravitation between two objects change if the distance between them is:
Made four times
What does a force do in the following case?
You catch a kicked ball.
Name and state the action and reaction in the following case:
Hammering a nail.
Is there a gravitational attraction between you and the book? Explain.
An apple falls towards the earth due to its gravitational force. The apple also attracts the earth with the same force. Why do we not see the earth rising towards the apple? Explain.
Particles of masses 2M, m and M are respectively at points A, B and C with AB = ½ (BC). m is much-much smaller than M and at time t = 0, they are all at rest (Figure). At subsequent times before any collision takes place ______.

Four identical particles of equal masses 1 kg made to move along the circumference of a circle of radius 1 m under the action of their own mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each particle will be ______.
If three equal masses m are placed at the three vertices of an equilateral triangle of side 1/m then what force acts on a particle of mass 2m placed at the centroid?
