Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What happens to the resistance, as the conductor is made thicker?
उत्तर
The resistance of a conductor is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the conductors. Hence, resistance is inversely proportional to the square of the radius of the conductor.
R ∝ \(\frac{1}{A}\)
R ∝ \(\frac{1}{r^2}\)
When a conductor is made thicker, the radius will be increased and so its resistance will be decreased.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
How does the resistance of a wire depend on its radius? Explain your answer.
Name three factors on which resistance of a given wire depends and state how is it affected by the factors stated by you.
Draw a I–V graph for a linear resistor. What does its slope represent?
Exercise.
The values of current (I) flowing through a resistor for various potential differences V across the resistor are given below. What is the value of resistor?
| I (ampere) | 0.5 | 1.0 | 2.0 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| V (volt) | 1.6 | 3.4 | 6.7 | 10.2 | 13.2 |
The effective resistance of three resistors connected in series is lesser than the lowest of the individual resistances.
An electric bulb is rated ‘240 V, 100 W’.
- What information can you get from the above statement?
- What will happen if this bulb is connected across 220 V?
- Calculate the resistance of the bulb.
- Also find the energy consumed by the bulb in 10 minutes.
Three resistors are connected in series with a cell. If the current in each resistor is 1.5A, then the current through the cell will be ______.
Observe the given circuit diagram and answer the questions that follow:
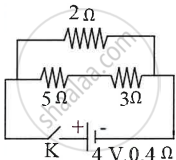
- Calculate the resistance of the circuit when the key K completes the circuit.
- Calculate the current through 3Ω resistance when the circuit is complete.
Define the term resistance.
Two copper wires are of the same length, but one is thicker than the other. Which wire will have more specific resistance?
