Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is a lever? How are the orders of the lever determined?
उत्तर
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a rigid rod that is capable of turning around a pivot called a fulcrum. It has three parts, namely effort, load, and fulcrum.
- Fulcrum: The rod of the lever rests on it and the lever rotates about it.
- Load: The weight lifted by the liver is called the load.
- Effort: The force applied on the other end of the rod to lift the load is called the effort.
The orders of the lever are determined depending on the position of the effort, the fulcrum, and the load.
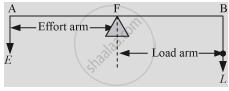
- Lever of the first order: When the fulcrum is situated between load and effort, we call it a lever of the first order. For example, beam balance, a crowbar, a see-saw."
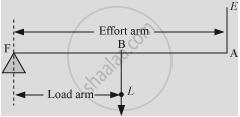
- Lever of second order: When the fulcrum and effort are situated at the two opposite ends of the lever and a load is placed in between them, we call it a lever of second order. For example, a nutcracker, a wheel-barrow, etc.
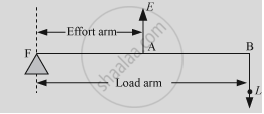
- Lever of the third order: When the fulcrum and load are situated at the opposite ends of the lever and an effort is applied somewhere between them, we call it a lever of the third order. For example, a pair of tongs, a fishing rod, etc.
संबंधित प्रश्न
State whether the following statement is True or False.
A machine performs work by itself.
Name six simple machines. Give an example of each machine.
Answer the following.
What do you understand by a complex machine?
State if the following statement is true or false. Correct the statement if it is false.
Work done by a machine is always more than the work done on a machine.
What do you understand by a simple machine?
Can a machine be 100% efficient?
Define Velocity Ratio
Define mechanical advantage (M.A.) of the machine.
Write an expression for the mechanical advantage of an inclined plane.
A cook used a ‘fire tong pair’ of length 32 cm. to lift a piece of burning coal of mass 500 g. If he applies his effort at a distance of 8 cm from the fulcrum, what is his effort? Assume friction etc. to be absent. Also, obtain values of the M.A. and the V.R. of this ‘machine’.
