Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer the following question.
What is meant by "diminishing returns to a factor"? Discuss any two reasons for the operation of diminishing returns to a factor.
उत्तर
The diminishing returns to a factor depict a particular phase under the law of variable proportion. Under this stage, the returns to a variable factor input or the marginal product is diminishing in nature, thereby giving the name ‘diminishing returns to a factor’.
This can be better understood with the help of the given diagram.
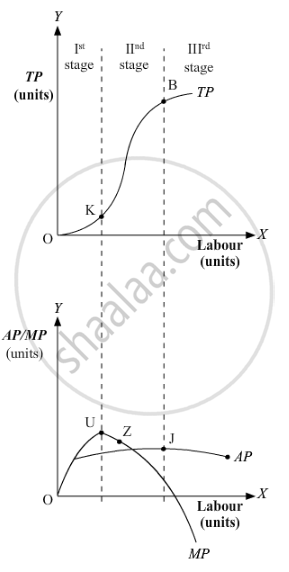
Here, the Diminishing Returns to a Factor is the stage that starts from point K and continues till point B on the TP curve. During this stage, the TP increases but at a decreasing rate and attains its maximum point at B, where it remains constant. On the other hand (in figure ii), the MP curve continues to fall and cuts AP from its maximum point Z, where MP equals AP. When TP attains its maximum point, corresponding to it, MP becomes zero. AP, in this stage initially rises, attains its maximum point at Z and thereafter starts falling.
Reasons for Decreasing Returns to a Factor:
- Fuller utilisation of fixed factor - In this stage, the fixed factor is utilised to its maximum level as more and more of labour inputs are employed.
- Imperfect substitutability between labour and capital - The variable factors are an imperfect substitute for the fixed factor. Therefore, the firm cannot substitute labour for capital and as a result, diminishing returns take place.
- Optimum Proportion/ Ideal Factor Ratio - The optimum proportion (or ideal factor ratio) is a fixed ratio in which the labour and capital inputs are employed. These factors will be the most efficient if they are employed as per the optimum proportion. If this proportion is disturbed (by combining more of labour inputs to the fixed units of capital), then the efficiency of the factors will fall, thereby leading to the diminishing returns to the factor.
संबंधित प्रश्न
The law of diminishing marginal utility can be explained with the help of schedule and diagram.
Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility with the help of a total utility schedule.
Explain the meaning of diminishing marginal rate of substitution with the help of an example.
Explain the importance of the law of Diminishing Marginal Utility.
What is the behaviour of Total Variable Cost, as output increases?
Assumption to the Law of diminishing Marginal util.
Exceptions to the Law of diminishing Marginal Util.
Answer with reason, whether you agree or disagree with the following statement.
The law of diminishing marginal utility depends upon assumptions.
Give reasons or explain the following statement:
In a rich country marginal propensity to consume is less.
State the following statement is True or False:
Negative MU denotes more satisfaction.
Answer in detail :
State and explain the law of Diminishing Marginal Utility. Explain its assumptions.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree:
There are no real exceptions to the law of Diminishing Marginal Utility.
State with reason whether you 'agree' or 'disagree' with the following statement.
Homogeneity of commodities is the only assumption of the law of diminishing marginal utility.
Answer the following question:
Explain the law of diminishing marginal utility using a hypothetical schedule.
Name the law which deals with the behaviour of marginal utility when the consumer consumes a commodity continuously at a given time. Explain this law with the help of a diagram.
