Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What is the form of that graph between
(i) K.E. and velocity for a constant mass?
(ii) K.E. and mass for a constant velocity?
उत्तर
(i) We have, for a constant mass,
K.E. ∝ v2
Hence, the graph is a parabola.
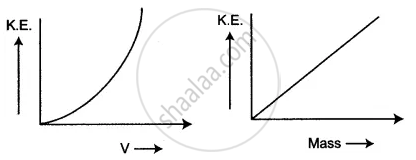
(ii) We have, for a constant velocity
K.E. ∝ m
Hence, the graph is a straight line.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Calculate the change in the Kinetic energy of a moving body if its velocity is reduced to 1/3rd of the initial velocity.
(i) The conversion of part of the energy into an undesirable form is called ______________.
(ii) For a given height h, __________________ the length l of the inclined plane, lesser will be the effort required.
Name the type of energy (kinetic or potential) possessed by the following:
Water flowing in a river.
Select the renewable and non-renewable sources of energy from the following:
Diesel
State two advantages of producing electricity from solar energy.
The following are some of the energy transformations.
A. Electrical to light
B. Work to heat
C. Chemical to light
D. Electrical to sound
E. Mechanical to electrical
Identify the energy transformation that takes place in the following by inserting the corresponding letter in the shape provided.
(i) A candle flame
(ii) A torch is lighted
(iii) A microphone is used in a meeting
(iv) A cycle dynamo
(v) A piece of metal is being filed
State the energy changes which take place when:
Water freezes in the freezing chamber of a fridge.
A body of mass 50 kg has a momentum of 3000 kg−1 ms. Calculate:
(j) the kinetic energy of the body.
(ii) the velocity of the body.
A ball of mass 50 g falls from a height of 2m and rebounds from the ground to 1.6 m. Find:
(i) The potential energy possessed by the ball when initially at rest.
(ii) The kinetic energy of the ball before it hits the ground.
(iii) The final potential energy of the ball.
(iv) The loss in kinetic energy of the ball on collision. (Take: g = 10N kg−1)
The solar cooker is an application of the ______ energy of the sun, while solar cells, solar lamps are applications of the ______ energy of the sun.
