Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What problems are being faced by the power sector in India?
उत्तर
The power sector is m faced with some critical challenges. These are as follows:
i. The installed capacity of India to generate electricity is not sufficient enough to meet an annual economic growth of 7%.
ii. The State Electricity Boards (SEBs) that distribute electricity suffered a great loss of more than Rs.500 billion due to transmission and distribution of electricity.
iii. The wrong pricing of electricity like supply of electricity at subsidised rates to agricultural sector and theft of electricity has exaggerated the problems of power sector.
iv. The high power tariffs and prolonged power cuts is another challenge in the power sector.
v. The thermal power station faces the scarcity of the raw materials to generate electricity.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What are the three basic sources of generating power?
What do you mean by transmission and distribution losses? How can they be reduced?
What are the various non-commercial sources of energy?
How has the consumption pattern of energy changed over the years?
Explain the various sources of energy in Tamil Nadu.
A uniform force of `(2hati + hatj)` N acts on a particle of mass 1 kg. The particle displaces from position `(3hatj + hatk)` m to `(5hati + 3hatj)` m. The work done by the force on the particle is ______
A ball of mass 1 kg and another of mass 2 kg are dropped from a tall building whose height is 80 m. After, a fall of 40 m each towards Earth, their respective kinetic energies will be in the ratio of ______
An engine pumps water continuously through a hose. Water leaves the hose with a velocity v and m is the mass per unit length of the water of the jet. What is the rate at which kinetic energy is imparted to water?.
If the potential energy of the particle is `α - β/2x^2`, then the force experienced by the particle is ______
A particle is placed at the origin and a force F = kx is acting on it (where k is a positive constant). If U(0) = 0, the graph of U(x) versus x will be (where U is the potential energy function)
A particle that is constrained to move along the x-axis, is subjected to a force in the same direction which varies with the distance x of the particle from the origin as F(x) = -kx + ax3. Here, k and a are positive constants. For x ≥ 0, the functional form of the potential energy U(x) of the particle is ______
Write the differences between conservative and Non-conservative forces. Give two examples each.
Define the following:
Law of conservation of energy
Define the following:
loss of kinetic energy in an inelastic collision.
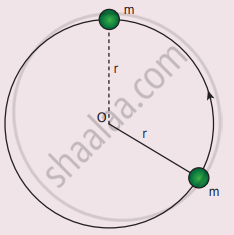
A bob of mass m is attached to one end of the rod of negligible mass and length r, the other end of which is pivoted freely at a fixed center O as shown in the figure. What initial speed must be given to the object to reach the top of the circle? (Hint: Use law of conservation of energy). Is this speed less or greater than the speed obtained in section 4.2.9?
Which of the following sector was the largest consumer of commercial energy in 1953-54?
Which of the following is a commercial source of energy?
Which of the following reforms has been initiated recently to meet the energy crisis in India?
The ______ is usually instituted via law and is typically applied to necessary goods like food, rent, and energy sources in order to ensure that everyone has access to them.
