Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What type of deviation from Roult’s Law is expected when phenol and aniline are mixed with each other? What change in the net volume of the mixture is expected? Graphically represent the deviation.
उत्तर
Negative Deviation is expected when phenol and aniline are mixed with each other. The net volume of the mixture will decrease, ΔV < 0 due to stronger intermolecular interactions.
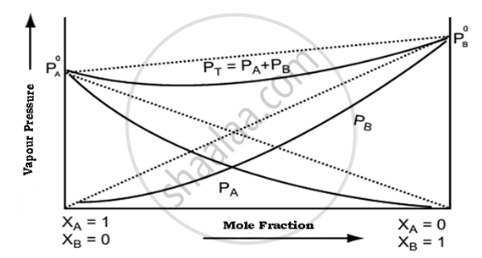
Diagram showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Vapour pressure of pure acetone and chloroform at 328 K are 741.8 mm Hg and 632.8 mm Hg respectively. Assuming that they form ideal solution over the entire range of composition, plot `"P"_"total"`, `"P"_"chloroform"` and `"P"_"acetone"` as a function of `"x"_"acetone"`. The experimental data observed for different compositions of mixtures is:
| `bb(100 xx "x"_"acetone")` | 0 | 11.8 | 23.4 | 36.0 | 50.8 | 58.2 | 64.5 | 72.1 |
| `bb("P"_"acetone"//"mm Hg")` | 0 | 54.9 | 110.1 | 202.4 | 322.7 | 405.9 | 454.1 | 521.1 |
| `bb("P"_"chloroform"//"mm Hg")` | 632.8 | 548.1 | 469.4 | 359.7 | 257.7 | 193.6 | 161.2 | 120.7 |
Plot this data also on the same graph paper. Indicate whether it has a positive or negative deviation from the ideal solution.
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
Ideal solutions obey ………. law and they …………. form azeotropic mixtures.
(Henry’s, aldol condensation, absence, do not, ohm, Raoult’s, increases, common ion effect, easily, three, solubility product, ohm-1, two, four, ohm-1, cm2, Cannizzaro, ohm-1 cm-1, zero, decreases, presence)
The rate at which a solid dissolves in liquid does not depend on ____________.
Assertion: Molarity of a solution in liquid state changes with temperature.
Reason: The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature.
Explain the terms ideal and non-ideal solutions in the light of forces of interactions operating between molecules in liquid solutions.
Dissociation constant and molar conductance of an acetic acid solution are 1.78 × 10–5 mol L–1 and 48.15 S cm–2 mol–1 respectively. The conductivity of the solution is (considering molar conductance at infinite dilution is 390.5 S cm–2 mol–1)
The pH of a solution of hydrochloric acid is 1.5. Calculate the concentration of the acid.
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
I2 and CCl4
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
NaClO4 and water
Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pair.
methanol and acetone
