Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
What would happen and why, to an electric bulb when it is connected across a supply of voltage (i) lower (ii) higher than its proper rating?
उत्तर
We know, Current = Voltage/Resistance
For a given bulb, the filament would have a definite characteristic resistance. Hence
(i) When the bulb is connected to a lower voltage supply, it would draw less current than its ‘proper current’. Hence it would not glow to its full capacity.
(ii) When the bulb is connected to a higher voltage supply, it would draw more current than its ‘proper current’. Hence its filament would get heated to a temperature higher than its proper permitted limit and is, therefore, likely to melt or fuse.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
State the S.I. unit of electrical power.
Fig . shows the essent ial features of a battery operated bell. The hammer strikes the gong when the swi tch is closed . State and explain the effect of using the following material successively to form the core.
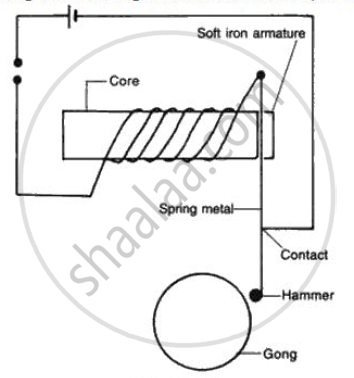
(a) Plastic
(b) Steel
(c) Copper
What does the unit kilowatt hour measure? Define it.
Mention three uses of the carbon arc.
Name two common material used for heating elements.
Why is a concave reflector placed behind the heating element in a room heater.
Why is the electric power from the generating station transmitted at high voltage?
Three 250 W heaters are connected in parallel to a 100 V supply, Calculate total current taken from the supply.
How can electric energy consumed by an electric appliance be calculated in kilowatt hour (kWh)?
The equation I2R seems to suggest that the rate of heating in a resistor is reduced if resistance decreases, whereas equation P = V2/R suggests just the opposite. How do you reconcile this problem?
