Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
उत्तर
The ratio of number of turns NS in secondary coil to the number of turns NP in the primary coil (NS / NP) is called the turns ratio.
A transformer cannot be used with direct current (d.c.) since its working is based on the principle that when there is a change of magnetic field lines due to varying current of same in one coil, an induced varying current of same frequency flows in the other coil. If the current in one coil is constant (i.e. d.c.), no induced current will flow in the other coil since there will be no change in the magnetic field lines linked with the coil.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When a wire is moved up and down in a magnetic field, a current is induced in the wire. What is this phenomenon known as?
A conducting rod is moved with a constant velocity v in a magnetic field. A potential difference appears across the two ends _____________ .
Draw a simple labeled diagram of a step-up transformer.
The diagram 10 shows two coils X and Y. The coil X is connected to a battery S and a key K. The coil Y is connected to a galvanometer G.
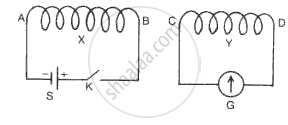
When the key K is closed. State the polarity
(i)At the end of the coil X,
(ii)At the end C of the coil Y,
(iii)At the end C of the coil Y if the coil Y is (a) Moved towards the coil X, (b) Moved away from the coil X.
Obtain an expression for motional emf from Lorentz force.
A closely wound circular coil of radius 0.02 m is placed perpendicular to the magnetic field. When the magnetic field is changed from 8000 T to 2000 T in 6 s, an emf of 44 V is induced in it. Calculate the number of turns in the coil.
We can induce the current in a coil by ____________.
A rectangular, a square, a circular and an elliptical loop, all in the (x - y) plane, are moving out of a uniform magnetic field with a constant velocity `vecv = vhati`. The magnetic field is directed along the negative z-axis direction. The induced emf, during the passage of these loops, out of the field region, will not remain constant for ______.
AB is a coil of copper wire having a large number of turns. The ends of the coil are connected with a galvanometer as shown. When the north pole of a strong bar magnet is moved towards end B of the coil, a deflection is observed in the galvanometer.

- State the reason for using galvanometer in the activity and why does its needle deflects momentarily when magnet is moved towards the coil.
- What would be observed in the galvanometer in a situation when the coil and the bar magnet both move with the same speed in the same direction? Justify your answer.
- State the conclusion that can be drawn from this activity.
Will there be any change in the momentary deflection in the galvanometer if number of turns in the coil is increased and a more stronger magnet is moved towards the coil?
OR
What is electromagnetic induction? What is observed in the galvanometer when a strong bar magnet is held stationary near one end of a coil of large number of turns? Justify your answer.
