Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why is the luminous efficiency small for a filament bulb as compared to a mercury vapour lamp?
उत्तर
In a filament bulb, heat energy is converted into light energy. Most of the electrical energy supplied to the bulb is radiated as heat and only a small percentage is radiated as visible light. Since heat waves are not visible, they don't contribute to visibility. Thus, its luminous flux is lesser than the total radiant flux; hence, its luminous efficiency is low.
In a mercury vapour lamp, a greater amount of electrical energy supplied is converted into visible radiation. Thus, its luminous flux is relatively higher than incandescent lamps.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
What is the luminous flux of a source emitting radio waves?
The luminous flux of a 1 W sodium vapour lamp is more than that of a 10 kW source of ultraviolet radiation. Comment.
A bulb is hanging over a table. At which portion of the table is the illuminance maximum? If a plane mirror is placed above the bulb facing the table, will the illuminance on the table increase?
The sun is less bright at morning and evening as compared to at noon although its distance from the observer is almost the same Why?
The yellow colour has a greater luminous efficiency as compared to the other colours. Can we increase the illuminating power of a white light source by putting a yellow plastic paper around this source?
The intensity produced by a long cylindrical light source at a small distance r from the source is proportional to _________ .
A room is illuminated by an extended source. The illuminance at a particular portion of a wall can be increased by
(a) moving the source
(b) rotating the source
(c) bringing some mirrors in proper positions
(d) changing the colour of the source.
Mark the correct options.
(a) The luminous efficiency of a monochromatic source is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(b) The luminous efficiency of a monochromatic source of wavelength 555 nm is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(c) The illuminating power of a monochromatic source of wavelength 555 nm is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
(d) The illuminating power of a monochromatic source is always greater than that of a white light source of same power.
Using figure, find the relative luminosity of wavelength (a) 480 nm, (b) 520 nm (c) 580 nm and (d) 600 nm.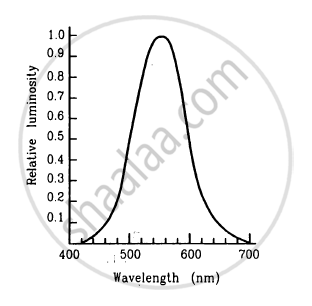
The luminous flux of a monochromatic source of 1 W is 450 lumen watt−1. Find the relative luminosity at the wavelength emitted.
The illuminance of a small area changes from 900 lumen m−2 to 400 lumen m−2 when it is shifted along its normal by 10 cm. Assuming that it is illuminated by a point source placed on the normal, find the distance between the source and the area in the original position.
Light from a point source falls on a small area placed perpendicular to the incident light. If the area is rotated about the incident light by an angle of 60°, by what fraction will the illuminance change?
A student is studying a book placed near the edge of a circular table of radius R. A point source of light is suspended directly above the centre of the table. What should be the height of the source above the table so as to produce maximum illuminance at the position of the book?
Two light sources of intensities 8 cd and 12 cd are placed on the same side of a photometer screen at a distance of 40 cm from it. Where should a 80 cd source be placed to balance the illuminance?
Choose the correct answer from given options
Photo diodes are used to detect
Light travels through a glass plate of thickness t and having a refractive index μ. If c is the velocity of light in vacuum, the time taken by the light to travel this thickness of glass is ______.
