Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Will the focal length of a lens for red light be more, same or less than that for blue light?
उत्तर
The refractive index depends on colour of light or wavelength of light.
Cauchy's equation: `mu = A+ B/lambda^2 + C/lambda^4 + ...`
As λred > λblue hence μred < μblue
Hence parallel beams of light incident on alens will be bent more towards the axis for blue light compared to red.
By lens maker's formula,
`1/f = (mu - 1)(1/R_1 - 1/R_2)`
The refractive index for red light is less than that for blue light μred < μblue
Hence `1/f_("red") < 1/f_("blue") ⇒ f_("red") > f_("blue")`
Thus, the focal length for red light will be greater than that for blue light.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A beam of light converges at a point P. Now a lens is placed in the path of the convergent beam 12 cm from P. At what point does the beam converge if the lens is
- a convex lens of focal length 20 cm, and
- a concave lens of focal length 16 cm?
An object of size 3.0 cm is placed 14 cm in front of a concave lens of focal length 21 cm. Describe the image produced by the lens. What happens if the object is moved further away from the lens?
You have learnt that plane and convex mirrors produce virtual images of objects. Can they produce real images under some circumstances? Explain.
A card sheet divided into squares each of size 1 mm2 is being viewed at a distance of 9 cm through a magnifying glass (a converging lens of focal length 9 cm) held close to the eye.
- What is the magnification produced by the lens? How much is the area of each square in the virtual image?
- What is the angular magnification (magnifying power) of the lens?
- Is the magnification in (a) equal to the magnifying power in (b)? Explain.
Figure shows an equiconvex lens (of refractive index 1.50) in contact with a liquid layer on top of a plane mirror. A small needle with its tip on the principal axis is moved along the axis until its inverted image is found at the position of the needle. The distance of the needle from the lens is measured to be 45.0 cm. The liquid is removed and the experiment is repeated. The new distance is measured to be 30.0 cm. What is the refractive index of the liquid?
A double convex lens of + 5 D is made of glass of refractive index 1.55 with both faces of equal radii of curvature. Find the value of its radius of curvature.
Two concave lenses L1 and L2 are kept in contact with each other. If the space between the two lenses is filled with a material of smaller refractive index, the magnitude of the focal length of the combination
An object approaches a convergent lens from the left of the lens with a uniform speed 5 m/s and stops at the focus. The image ______.
An unsymmetrical double convex thin lens forms the image of a point object on its axis. Will the position of the image change if the lens is reversed?
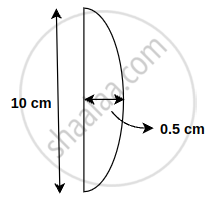
A plano convex lens has diameter of 10 cm and its thickness at the centre is 0.5 cm. Speed of light in the lens is 2 × 108 ms-1. What is the focal length of the lens?