Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With the help of circuit diagram explain the working principle of a transistor amplifier as an oscillator.
उत्तर
The circuit diagram for a transistor amplifier as an oscillator is represented as
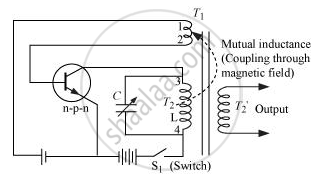
In an oscillator, a sustained Α.C. output is obtained without any input oscillation. For this to happen, the output of a transistor amplifier is fed back into its input. This is achieved by coupling the winding T1 to winding T2.
When key S1 is closed, the collector current begins to increase, which supports the forward bias of the emitter−base circuit. Collector current increases until it reaches saturation. When the saturation is reached, the magnetic flux linked to winding T1 becomes steady. Hence, the forward bias of the emitter−base circuit is no longer supported. The transistor is now driven into cut-off. This cycle repeats itself and an oscillating output is obtained.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
For transistor action, which of the following statements are correct:
(a) Base, emitter and collector regions should have similar size and doping concentrations.
(b) The base region must be very thin and lightly doped.
(c) The emitter junction is forward biased and collector junction is reverse biased.
(d) Both the emitter junction as well as the collector junction are forward biased.
Describe briefly with the help of a circuit diagram, how the flow of current carriers in a p-n-p transistor is regulated with emitter-base junction forward biased and base-collector junction reverse biased.
In oscillatory circuit, reactive components are connected in
