Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to the discovery of the structure of an atom, explain in brief – William Crookes experiment for the discovery of cathode rays, followed by – J.J. Thomsons experiment pertaining to the constituents of the cathode rays. State which sub-atomic particle was discovered from his experiment.
उत्तर
Electrons were discovered in 1897 by J.J. Thomson when he was studying the properties of cathode rays.
Earlier, William Crooks, another British scientist, had performed an experiment to study the phenomenon of electric discharge through gases. He observed that when an electric current of high voltage was passed through a discharge tube (a glass tube sealed at both ends with metal plates) containing a gas at very low pressure (0·01 mm of mercury), rays were emitted from the negative terminal called cathode. He called these rays 'cathode rays'.
J.J. Thomson studied the characteristics and the constituents of the cathode rays and concluded that: Cathode rays consist of negatively charged particles (now called electrons), present in atoms of all the elements.
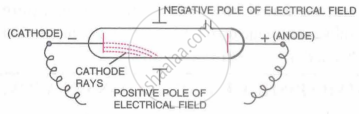
J.J. Thomson's Experiment: An electric field was applied in the path of cathode rays in the discharge tube. It was observed that cathode rays were deflected towards the positive plate of the electric field. This showed that cathode rays were negatively charged.
When a magnetic field was applied in the path of cathode rays, they were again deflected in a direction in which moving negative charge would be deflected.
This proved that cathode rays contained negatively charged particles called electrons.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Fill in the blank
The outermost shell of an atom is known as............................
Fill in the blank
Neutrons are .......................... particles having mass equal to that of protons.
Give the following a suitable word/phrase.
The sum of the number of protons and neutrons of an atom.
Mention briefly the salient features of Dalton’s atomic theory (five points)
Tick the most appropriate answer.
How many times is a proton heavier than an electron?
- 1500
- 1800
- 1840
- none of these
WRITE SHORT ANSWER
Name the isotopes of hydrogen.
Draw the electronic configuration of the following elements clearly stating the number of neutrons and protons in their nucleus.
a. Beryllium b. Silicon
c. Chlorine d. Aluminium
e. Nitrogen
Compare an electron, a proton and a neutron in respect of their relative masses and charges.
Define the term Mass number.
Write down the names of the particles represented by the following symbols and explain the meaning of superscript and subscript numbers attached.
`""_1"H"^1`, `""_0"n"^1`,`""_(-1)"e"^0`
