Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
With reference to the levels of an organisation, differentiate between living organisms and non-living objects.
उत्तर
The organisation is a systematic arrangement of smaller and simpler components into a larger one in a hierarchy or pyramid of levels where each level is formed of components of a lower level and itself becomes part of a higher-level for achieving a common goal.
Three levels of organisation are met in nature – physical biological and ecological. At every level two types of questions arise – how (mechanism of the process) and why (significance of the process).
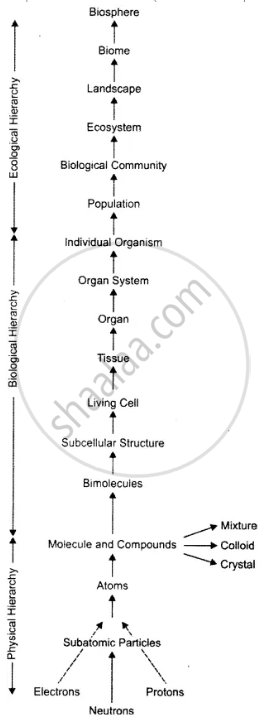
Various levels of organisation.
The non-living objects occur as molecules and compounds which are found as mixture, colloids, and crystals. They are formed of atoms, atoms are formed of subatomic particles, which are ^ composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons the lowest structures.
In the living organisation, the molecules and g compounds polymerise and aggregate to form o’ biomolecules. The different biomolecules aggregate and organise to form different subcellular structures (= organelles) which together constitute the first living component of the cell (individual unicellular organism). The cells may be held together to form tissue and different tissues together form organs.
The different organs constitute an organ system § and different organ systems form a multicellular ± complex whole Called individual organism the basic unit of ecology. if An aggregation of individuals of the same species is m called population. The assemblage of a population of different species present in an area is called Biological Community.
The different biological communities and the physical environment both get integrated to form a self-sufficient, self-regulated fragment of nature, called the ecosystem.
The different ecosystems characterised by specific climatic zone, form a major category of regional gecological organisation called Biome. Biomes are of two types-terrestrial and aquatic.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Why the pyramid of energy is always upright? Explain.
Which organisms constitute the last trophic level?
Answer the following question.
Write any two limitations of ecological pyramids.
'The pyramid of energy is always upright.' Explain
Give an example of an ecosystem that shows an inverted pyramid of numbers.
Give an example of an ecosystem that shows an inverted pyramid of biomass.
Pyramid of biomass in terrestrial ecosystem shows sharp decline in
In an aquatic ecosystem, a mollusc typically belongs to-
Pyramid of numbers is ______.
(a) Given below is a pyramid of biomass in an ecosystem where each bar represents the standing crop available in the trophic level. With the help of an example explain the conditions where this kind of pyramid is possible in nature.
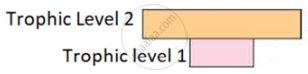
(b) Will the pyramid of energy be also of the same shape in this situation? Give a reason for your response.
