Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Work out a cross to explain how normal parents may have a sickle-cell anaemic child.
उत्तर
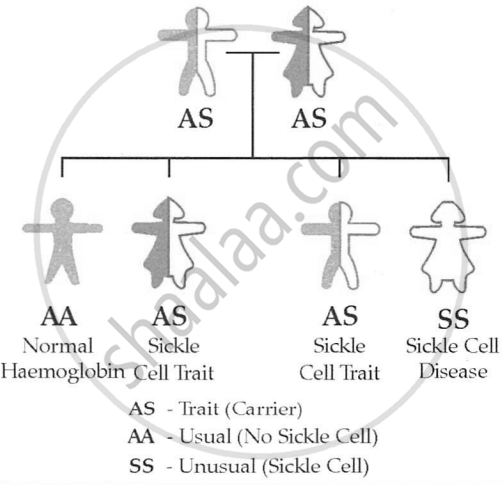
Sickle-cell anemia is an autosomal recessive genetic illness, which means that individuals must inherit two copies of the mutant allele (one from each parent) in order to develop the disorder. To have a kid with sickle-cell anemia, both parents must be carriers of the sickle-cell trait (heterozygous). Let's refer to the normal allele as H and the sickle-cell allele as S. Normal parents with the sickle-cell trait (heterozygous: HbA/S) have the following genetic makeup:
Father: HbAHbS Mother: HbAHbS
When these parents produce offspring, there are four possible combinations of alleles in their offspring:
- HbAHbA (normal)
- HbAHbS (carrier, asymptomatic)
- HbSHbA (carrier, asymptomatic)
- HbSHbS (affected with sickle-cell anemia)
In this case, there is a 25% chance, or 1 in 4, that the child will get sickle-cell anemia because they will receive two copies of the sickle-cell allele (HbSHbS).