Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Write a note on the formation of α-helix.
उत्तर
1. In the α-helix substructure, the amino acids are arranged in a right-handed helical (spiral) structure and are stabilized by the hydrogen bond between the carbonyl oxygen one amino acid (nth residue) with amino hydrogen of the fifth residue (n + 4th residue).
2. The side chains of the residues protrude outside of the helix. Each turn of an α-helix contains about 3.6 residues and is about 5.4 Å long.
3. The amino acid proline produces a line in the helical structure and is often called a helical breaker due to its rigid cyclic structure.
4. Many fibrous proteins such as α-Keratin in hair, nails, wool, skin, and myosin in muscles have α-helix structure. The stretching property of human hair is due to the helical structure of α-keratin in hair.
5. Structure of α-helix

Secondary structure of proteins
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The following statement applies to DNA only, some to RNA only, and some to both. Label them accordingly.
The polynucleotide is double stranded. (_______)
Write the sequence of the complementary strand for the following segment of a DNA molecule.
5' - CGTTTAAG - 3'
In which of the following RNA is genetic material?
Identify the CORRECT statement.
Purine derivative among the following bases is ____________.
What is the number of \[\begin{array}{cc}\\\backslash\phantom{.......}\\\phantom{}\ce{C = O}\\/\phantom{........}\end{array}\] groups present in nitrogen bases of nucleic acids, thymine and uracil respectively?
If Adenine makes 30% of the DNA molecule, what will be the percentage of Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine in it?
Refer to the given figure.
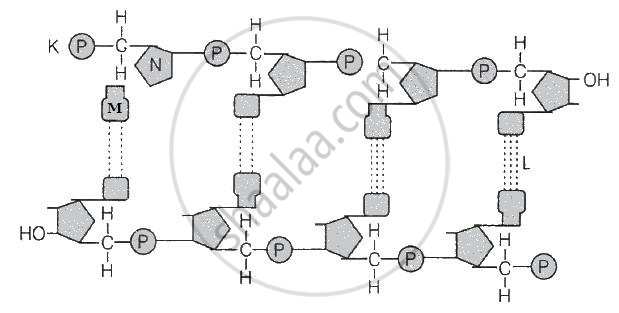
Select the option which correctly identifies.
Watson and Crick (1953) proposed DNA double helix model and won the Nobel Prize; their model of DNA was based on:
- X-ray diffraction studies of DNA were done by Wilkins and Franklin.
- Chargaff’s base equivalence rule
- Griffith's transformation experiment
- Meselson and Stahl's experiment
What are the nucleotides?
