Advertisements
Advertisements
In the Brahmaputra river basin, floods are almost an annual feature. Give two reasons to explain why.
Concept: Relief and Drainage
Answer the following question:
Briefly explain the geological evolution of the peninsular plateau.
Concept: Geological Formation
Answer the following question.
Name the two rivers that make the easternmost and the westernmost limits of Kumaon Himalayas.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
(i) Where is the New Mangalore Port located?
(ii) What is the chief importance of this port?
Concept: Geological Formation
Name the following :
A pilgrimage center in Himachal Pradesh.
Concept: Geological Formation
Name the following :
A historic place in Rajasthan.
Concept: Geological Formation
Name the following :
An important hill resort of West Bengal.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
Answer the following question:
Define the terms Lagoon and Delta with an example of each from the Indian region.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
With reference to river Godavari, name the following :
The State where it forms its delta.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
Refer to the outline Map of India provided and answer the following questions on the Map:
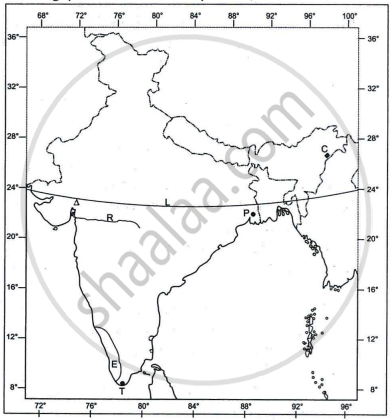
- Mark and label the following on the given map of India.
- The coastal plain that receives rainfall from Northeast monsoons.
- The oldest mountain range of India.
- The plateau rich in minerals in India.
- The angular value of the latitude marked L is ______.
- 37°4' N
- 68°7' N
- 8°4' N
- 23°30' N
- The riverine port marked P is ______.
- Kolkata
- Kochi
- Vishakhapatnam
- Chennai
- The cotton textile centre marked by the Δ is ______.
- Mumbai
- Coimbatore
- Pune
- Ahmedabad
- The state marked E has the highest ______.
- literacy rate.
- index of concentration of population.
- density of population
- level of urbanisation.
- Identify the following:
- The city marked T, which is one of the terminals of the North-South corridor, is ______.
- The oldest oilfield of India marked C is ______.
- The west flowing river marked R between the Vindhyas and the Satpura range is ______.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
The main Standard geological era is ______.
Concept: Geological Formation
River Brahmaputra is a tributary of River Ganga.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
Mention any two characteristics features of the Himalayas.
Concept: Geological Formation
Study the sketch map given below and answer the questions that follow:
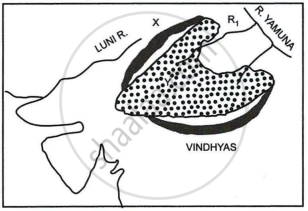
- Identify the dotted region marked Y. Mention any three of its characteristic features.
- Name the mountain range marked X, the river marked R1 and the type of rock that constitutes the dotted region.
Concept: Geological Formation
Study the sketch map given below and answer the questions that follow:
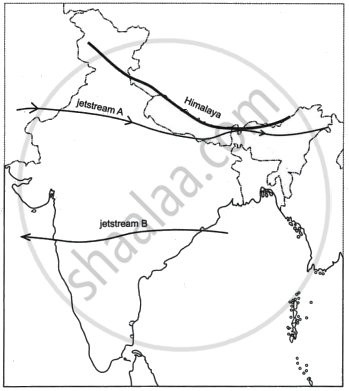
- State the direction of the movement of the jetstreams A and B in the Indian region. Give reasons for the same.
- How do the jetstreams A and B influence the Indian climate?
Concept: Geological Formation
Assertion: The Himalayas were formed due to the collision of tectonic plates.
Reason: Indian plate moved northwards and pushed beneath the Eurasian Plate leading to the compression of sediments in the Tethys Sea.
Concept: Geological Formation
India is referred to as a sub-continent. Justify.
Concept: Geological Formation
How is the Himalayan River system different from the Peninsular River system?
Concept: Geological Formation
Assertion: The rivers on the western coast carry a lot of sediments but do not form a delta.
Reason: They have a large catchment area and form estuaries.
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
There are great contrasts observed between the Himalayan and Peninsular rivers of India. How do these differences impact human settlements?
Concept: Major Physiographic Divisions and Their Characteristics
