Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Study the sketch map given below and answer the questions that follow:
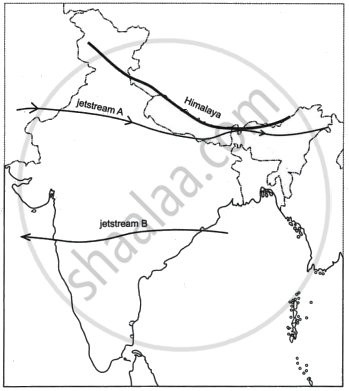
- State the direction of the movement of the jetstreams A and B in the Indian region. Give reasons for the same.
- How do the jetstreams A and B influence the Indian climate?
उत्तर
- Jetstream A, also referred to as the sub-tropical westerly jet stream, moves eastward from west to east and is primarily responsible for winter weather in northern India, which occurs south of the Himalayas. Heat-producing tropical air masses and frigid polar air masses diverge in temperature, which leads to its formation. During the summer, sub-tropical easterly jet stream B, which flows from east to west, blows over peninsular India at a latitude of roughly 14°N. It forms as a result of the temperature differential between the warm tropical air masses and the polar air masses.
- The following are the effects of jetstreams A and B, or the sub-tropical easterly and westerly jet streams, on India's climate:
- The upper air circulation, which is dominated by Sub-tropical jetstreams (STJ), is what determines when the monsoon begins. The jetstreams have an impact on this. The tropical easterly jetstream is directly linked to India's south-west monsoon.
- The winter monsoon, also known as the north-east monsoon, is associated with the subtropical westerly jet stream region. Because the wind is cold, there is a lot of pressure at the surface. The chilly winter waves that flow through the northern regions of the nation, including UP and Bihar, are also caused by these winds. The north-east monsoon is brought on by westerly jetstreams that enter the Bay of Bengal. The humidity from the Bay of Bengal causes rainfall when this wind reaches Tamil Nadu's coast.
- Western cyclonic disturbances in northern and northwestern India. This influence is caused by the subtropical westerly jet stream, which blows south of the Himalayas during the winter months (December-February).
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Name the four Indian geological eras in their chronological order.
Give reasons for the following
(i) There is a dense network of railways over the North Indian Plains.
(ii) Peninsular Plateau has a high proportion of metalled roads.
(iii) A good transport network promotes industrial development.
Answer the following question:
The figure below represents a topographic section from the Himalayas to the Peninsular region. Identify any two of the features marked A, B, C, and D.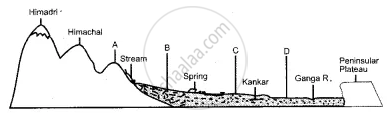
Answer the following question.
Give three differences between the Western and the Eastern Himalayas.
Name any two standard geological eras, along with their duration.
Answer the following question:
The figure below represents a section from the Aravalis to the Peninsular region.

Identify any two of the relief features marked, A, B, C, and D.
(i) Where is the New Mangalore Port located?
(ii) What is the chief importance of this port?
Study the sketch map given below and answer the questions that follow:
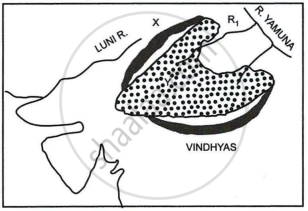
- Identify the dotted region marked Y. Mention any three of its characteristic features.
- Name the mountain range marked X, the river marked R1 and the type of rock that constitutes the dotted region.
How is the Himalayan River system different from the Peninsular River system?
Identify the image given below and explain the formation of this geological division in India.

