Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 - Demand Analysis SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 - Demand Analysis - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-12-standard-hsc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 3.1: Demand Analysis
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 3.1 of Maharashtra State Board SCERT Maharashtra for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Choose the correct option
Choose the correct option
Statements that explain Giffen’s paradox:
- It is an exception to the law of demand.
- It is applicable to inferior or low quality goods.
- Demand increases when the prices of inferior goods fall
- It was identified by Prof. Alfred Marshall.
Only a
a, b
b, c, d
a, b, c, d
Statements related to decrease in demand
- It is a type of change in demand
- It takes place due to unfavourable changes in other factors like tastes, income etc.
- Price remains constant
- Demand curve shifts to the right hand side of the original demand curve
a, b, c, d
a, b, c
b, c, d
a, c, d
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Complete the correlation
Complete the correlation
Demand curve : ______ :: Supply curve : Upward
Tea and coffee : ______ :: Electricity : Composite demand
Steeper demand curve : Relatively inelastic demand :: Flatter demand curve: ______.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Give economic terms
Give economic terms
Total demand for a commodity from all the consumers at a given price during a given period of time −
Demand for a commodity which can be put to several uses −
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Find the odd word
Find the odd word
Assumptions to law of demand -
Constant level of income
No changes in taxation policy
No change in size of population
Cardinal measurement
Find the odd word
Types of demand -
Individual demand
Direct demand
Competitive demand
Complementary demand
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Complete the following statements
Complete the following statements
The demand for a commodity which can be put to several uses is known as ______.
Joint Demand
Composite Demand
direct demand
derived demand
The Law of Demand was introduced by ______.
Prof. Adam Smith
Prof. Alfred Marshall
Prof. Joan Robinson
Prof. Keynes
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Assertion and Reasoning type questions
Assertion and Reasoning type questions
Assertion (A): All desires are not demand.
Reasoning (R): In Economics, demand means a desire which is backed by willingness and ability to pay.
(A) is True but (R) is False.
(A) is False but (R) is True.
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
Assertion (A): Under exceptional cases, demand curve has a positive slope.
Reasoning (R): In exceptional cases, consumer buys more when the price of a commodity rises and buys less when the price of commodity falls.
(A) is True but (R) is False.
(A) is False but (R) is True.
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is the correct explanation of (A).
Both (A) and (R) are True and (R) is not the correct explanation of (A).
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Identify & explain the concepts from the given illustrations
Identify & explain the concept from the given illustration.
Kaushik purchased 10 kgs of wheat for his monthly consumption at ₹ 40/- per kg.
Identify & explain the concept from the given illustratio.
Aman purchased sewing machines and furniture for his tailoring shop.
Identify & explain the concept from the given illustration.
Manish purchased 100 metres of cotton textile to produce readymade shirts at his garment factory.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Distinguish Between
Distinguish between the following:
Direct demand and Indirect demand.
Distinguish Between
Joint/Complementary demand and Composite demand
Distinguish Between
Individual demand schedule and Market Demand Schedule
Distinguish Between
Demand curve and Supply Curve
Distinguish between:
Expansion of demand and Contraction of demand.
Distinguish between:
Increase in demand and Decrease in demand
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Answer the following
Explain any four types of demand.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis State with reasons whether you agree or disagree with the following statements
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
All desires are demand.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
When the prices of Giffen goods falls, demand for such goods rises.
Agree
Disagree
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement:
There are no exceptions to the law of demand.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement.
There is an inverse relationship between price and demand.
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis TABLES
4 MARKS EACH CORRECT ANSWER
Study the following table, figure, passage and answer the question given below it.
| Price of commodity ‘ X | Quantity of ‘X‘ in kgs. | Market demand | ||
|
Consumer A |
Consumer B |
Consumer C |
A+B+C | |
| 10 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 30 |
| 8 | 10 | 15 | ______ | 45 |
| 6 | ______ | 20 | 25 | 60 |
| 4 | 20 | ______ | 30 | 75 |
| 2 | 25 | 30 | 35 | ______ |
| 1 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 105 |
- Complete the table. (2m)
- Draw Market demand curve based on above Market demand schedule and label it. (2m)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis DIAGRAMS
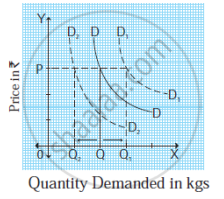
Questions:
- Demand Curve D1D1indicates ______ (1m)
- Demand Curve D2D2indicates______ (1m)
- Name the above diagram and explain. (2m)
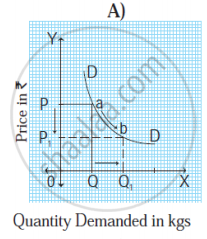 |
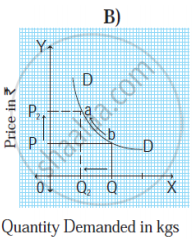 |
Questions:
- Diagram’ A ‘represents _____in demand (1m)
- Diagram ‘B’ represents _____in demand (1m)
- In diagram ‘A’ movement of demand curve is in_____ direction (1m)
- In diagram ‘B’ movement of demand curve is in______ direction (1m)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis PASSAGE
PASSAGE
Mona visits a shopping mall near her residence. She shops for monthly groceries which include rice, wheat, sugar, cooking oil and pulses. She purchases additional quantities of sugar much more than her monthly requirement anticipating that prices may rise in the coming days due to festivities.
She observes two different qualities of tur dal out of which one quality is inferior and the other is superior. She does not purchase the low quality tur dal even though its price is comparatively lower. Instead she prefers to buy superior quality tur dal.
- Identify the exception to the law of demand in the given passage with reference to purchase of additional quantities of sugar much more than monthly requirement anticipating that prices may rise in the coming days due to festivities (1mark)
- Identify the kind of good with reference to low quality tur dal (1mark)
- Express your personal opinion based on the above information. (2 marks)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC 3.1 Demand Analysis Answer in detail
Answer in detail
State and explain the ‘law of demand’ with its exceptions.
Solutions for 3.1: Demand Analysis
![SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 - Demand Analysis SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 - Demand Analysis - Shaalaa.com](/images/economics-english-12-standard-hsc_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 - Demand Analysis
Shaalaa.com has the Maharashtra State Board Mathematics Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. SCERT Maharashtra solutions for Mathematics Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board 3.1 (Demand Analysis) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. SCERT Maharashtra textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC chapter 3.1 Demand Analysis are Demand, Law of Demand, Exceptions to the Law of Demand, Demand Curve and Its Slope, Factors of Demand, Demand Schedule, Types of Demand, Determinants of Demand, Assumptions of Law of Demand, Variations in Demand, Change in Demand, Concept of Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply.
Using SCERT Maharashtra Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC solutions Demand Analysis exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in SCERT Maharashtra Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum Maharashtra State Board Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC students prefer SCERT Maharashtra Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 3.1, Demand Analysis Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC additional questions for Mathematics Economics [English] 12 Standard HSC Maharashtra State Board, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
