Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply.
- What is the rms value of current in the circuit?
- What is the net power consumed over a full cycle?
Solution
Resistance of the resistor, R = 100 Ω
Supply voltage, V = 220 V
Frequency, v = 50 Hz
a. The r.m.s. value of the current in the circuit is given as:
`"I" = "V"/"R"`
= `220/100`
= 2.20 A
b. The net power consumed over a full cycle is given as:
P = VI
= 220 × 2.2
= 484 W
RELATED QUESTIONS
A device 'X' is connected to an ac source V = V0 sin ωt. The variation of voltage, current and power in one cycle is shown in the following graph:

(a) Identify the device 'X'.
(b) Which of the curves A, B and C represent the voltage , current and the power consumed in the circuit? Justify your answer.
(c) How does its impedance vary with frequency of the ac source? Show graphically.
(d) Obtain an expression for the current in the circuit and its phase relation with ac voltage.
An alternative voltage given by V = 140 sin 314t is connected across a pure resistor of 50 Ω. Find
- The frequency of the source.
- The rms current is through the resistor.
A 100 Ω resistor is connected to a 220 V, 50 Hz ac supply.
What is the net power consumed over a full cycle?
Effective voltage Vrms is related to peak voltage Vo by ______.
If Vm and Im are peak voltage and current, impedance Z in an AC circuit is ______.
Study the circuits (a) and (b) shown in figure and answer the following questions.
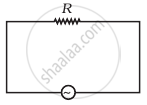 (a) |
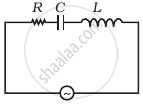 (b) |
- Under which conditions would the rms currents in the two circuits be the same?
- Can the rms current in circuit (b) be larger than that in (a)?
Can the instantaneous power output of an ac source ever be negative? Can the average power output be negative?
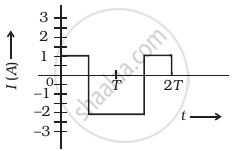
The alternating current in a circuit is described by the graph shown in figure. Show rms current in this graph.
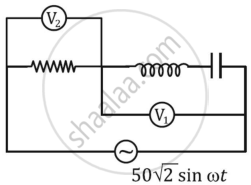
If the reading of the voltmeter V1 is 40 V, then the reading of voltmeter V2 is ______.